Business building block assembly
In the process of learning and development, every programmer knows the importance of decoupling and modularization, and also hopes that the programs designed and developed by themselves support modularization, and the developed modules can be quickly reused by others , in order to achieve this effect, we learn various modularization and decoupling technologies, from object-oriented design patterns to micro-service architecture. In recent years, everyone thinks that micro-service architecture is a modular silver bullet, and they are all transformed towards micro-service architecture. , but the actual effect is not only not very modular, but caught in the quagmire of application deployment and operation and maintenance.This article will talk about some new ideas for Rainbond to solve application architecture decoupling and modularization.
Problems of current business modularization and decoupling
- The degree of architectural coupling is still too high, and the decoupling is not complete.For example, the microservices disassembled through the microservice architecture are limited by the development language and microservice framework. They cannot be called across development languages, and cannot be used across frameworks. They are also limited by the deployment environment, and the deployment problem needs to be re-solved in another environment.
- Define the module from the developer's point of view, rather than the user's point of view, resulting in a bad user experience.Now the modules we define are usually defined by development. Since the development is far from the actual use scenario, we subjectively think that the modules are divided into small and small. No matter what the scenario requires, my module can be reused and satisfied, but from the user From an angle, the smaller and finer the modules are divided, the higher the cost of learning and use, or even impossible to use at all. Many modules are excessive disassembly and excessive design.
- Modular release is complex, and maintenance and upgrade costs are high.The current modularization itself is a development process, and both the definition and packaging processes require development participation, resulting in high costs.
Decoupling and Implementation Ideas Based on Rainbond Application Model
Rainbondis a cloud-native application management platform that can manage the entire application lifecycle.Below we explain in detail how Rainbond solves the above problems.
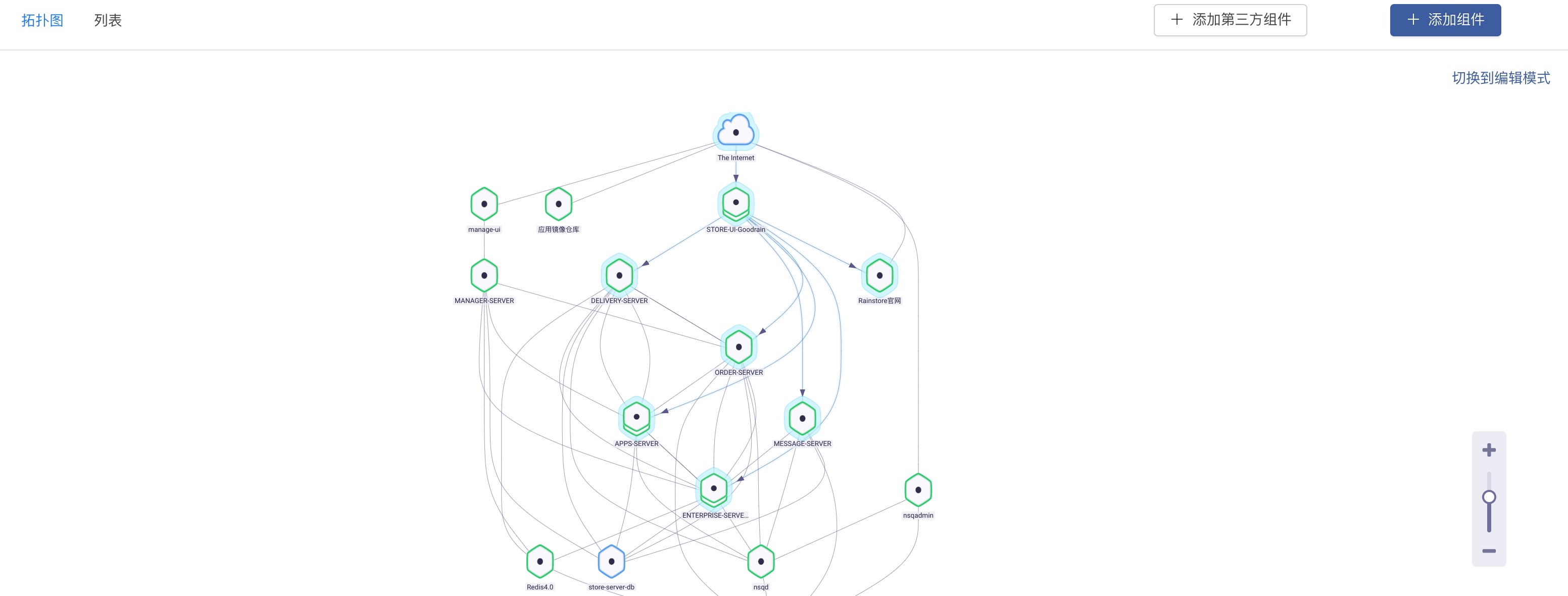
The core of Rainbond abstracts and defines a set of application models. The application model solves the problem of decoupling from the architecture. The application model completely decouples the application, operation and maintenance features and the underlying infrastructure. The application is assembled from multiple business components. Each business component can be developed in different languages and constructed in different ways, and can be assembled as long as it conforms to the business contract.Through the above decoupling methods, the business components, operation and maintenance capabilities and deployment environment are completely decoupled. The business components only need to focus on pure business and no longer care about matching different development frameworks, service governance functions, operation and maintenance tools and deployment due to differences in usage scenarios. Environment, business components, operation and maintenance capabilities, and deployment environments can be freely combined and assembled according to usage scenarios.
Assembly scene based on business components:
- From the development of business functions, business components provide services based on business protocols, which are not restricted by frameworks and development languages, and can be reused in other business scenarios;
- From the perspective of operation and maintenance management, in the development and test environment, there is no need to enable the operation and maintenance feature, and in the production environment, there are higher requirements for business governance, monitoring, performance, stability and security, which can be enabled on demand through the plug-in mechanism. operation and maintenance characteristics;
- From the deployment environment, the bottom layer of the application model implements the docking standard k8s API, and all infrastructure that conforms to the k8s standard API can be docked and deployed, which means that business components can be deployed to public cloud, private cloud and on edge devices.
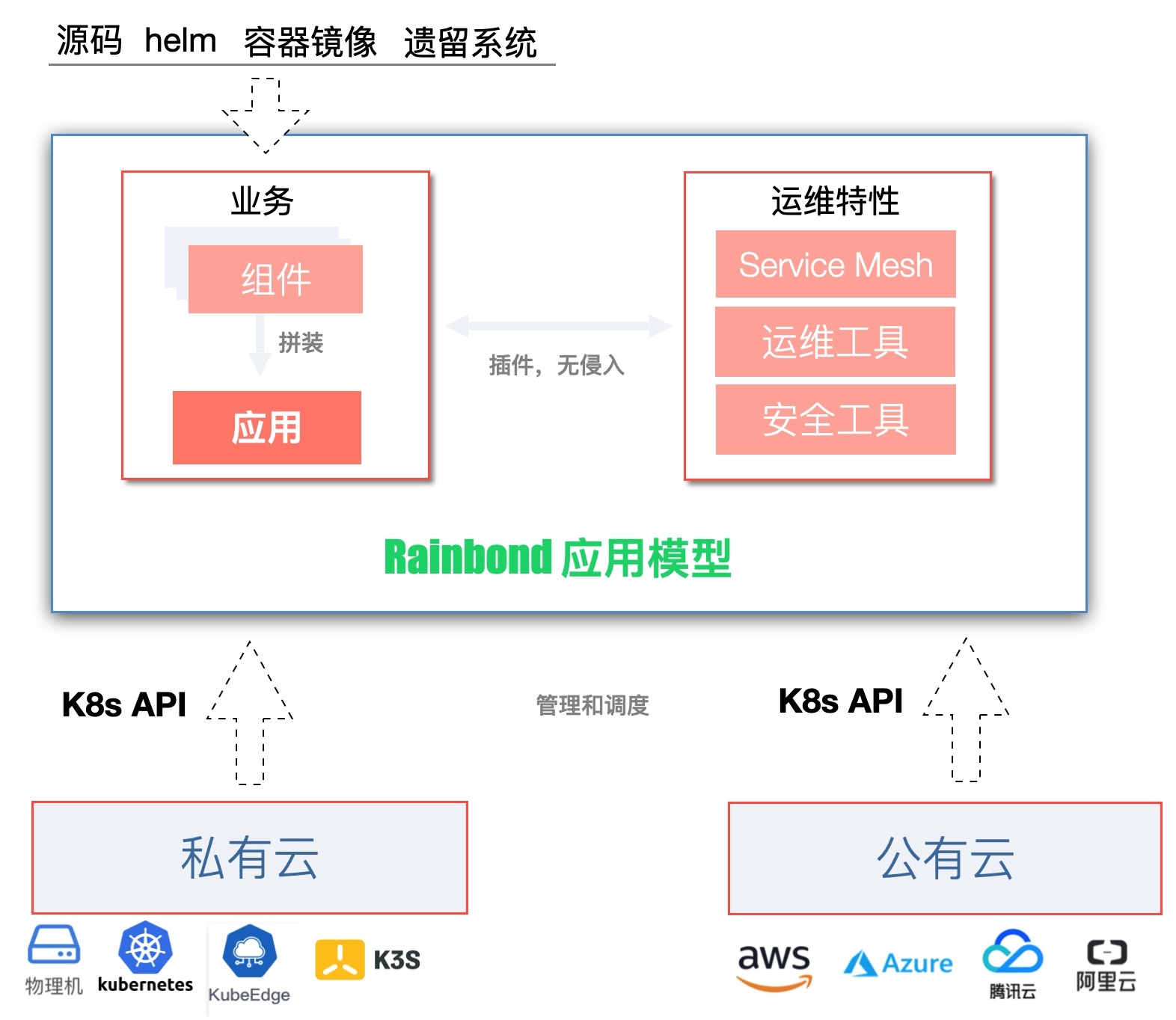
Decoupling can not only improve the flexibility of various scenarios, but also greatly improve the reuse rate of business components, operation and maintenance plug-ins, and infrastructure. When the accumulated reusable capabilities are more, we will face different scenarios and different users. And the responsiveness of different markets is also stronger.
Rainbond The application model follows the "application-centric" design concept, encapsulates the underlying complex technologies irrelevant to the application, and simplifies the understanding and use experience.Application models can be displayed and stored in the form of application templates, and the above reusable capabilities are released to the application market through application templates for others to use, thereby realizing module reuse.Usually, we mainly consider developers when implementing modularization, while application templates consider users more, abstract definitions from the user's point of view, so that users can use them, thereby driving the production of application templates.In terms of user experience, application templates can be installed and upgraded with one click, and business assembly can be realized by "drag and drop".Application templates are highly flexible. Application templates support different particle sizes. Templates and templates can be assembled to create new templates. New templates can also be continuously assembled. The size of the particles is determined by the user and given meaning by the user.
The application template has the ability to package business and has four characteristics:
- Modularization, which can form reusable capability units and assemble usage scenarios as needed.
- Autonomy, Self-sufficient, can be installed, upgraded and managed independently, ensuring the flexibility of combination.
- can be arranged, templates and templates can be assembled into new templates, with unlimited assembly capabilities.
- can be found, reflected in two ways: internal service and external service, accessible to business and technology, developers and other applications.
Application template definition and implementation content:
- Apply basic metadata
- name
- timestamp
- Version number and nickname
- resource usage
- Application governance mode (k8s service mode, Service Mesh built-in and Istio)
- Application Gateway Information
- external port
- Domain Names and Certificates
- release strategy
- Apply global configuration
- one or more business components
- Dependencies of business components
- Types of business components (source, images, Helm, and third-party APIs)
- How components are built
- How components are stored
- How components are configured
- How components work
- Plug-ins for business components
- Component ports and protocols
- component environment variables
Module release and assembly process
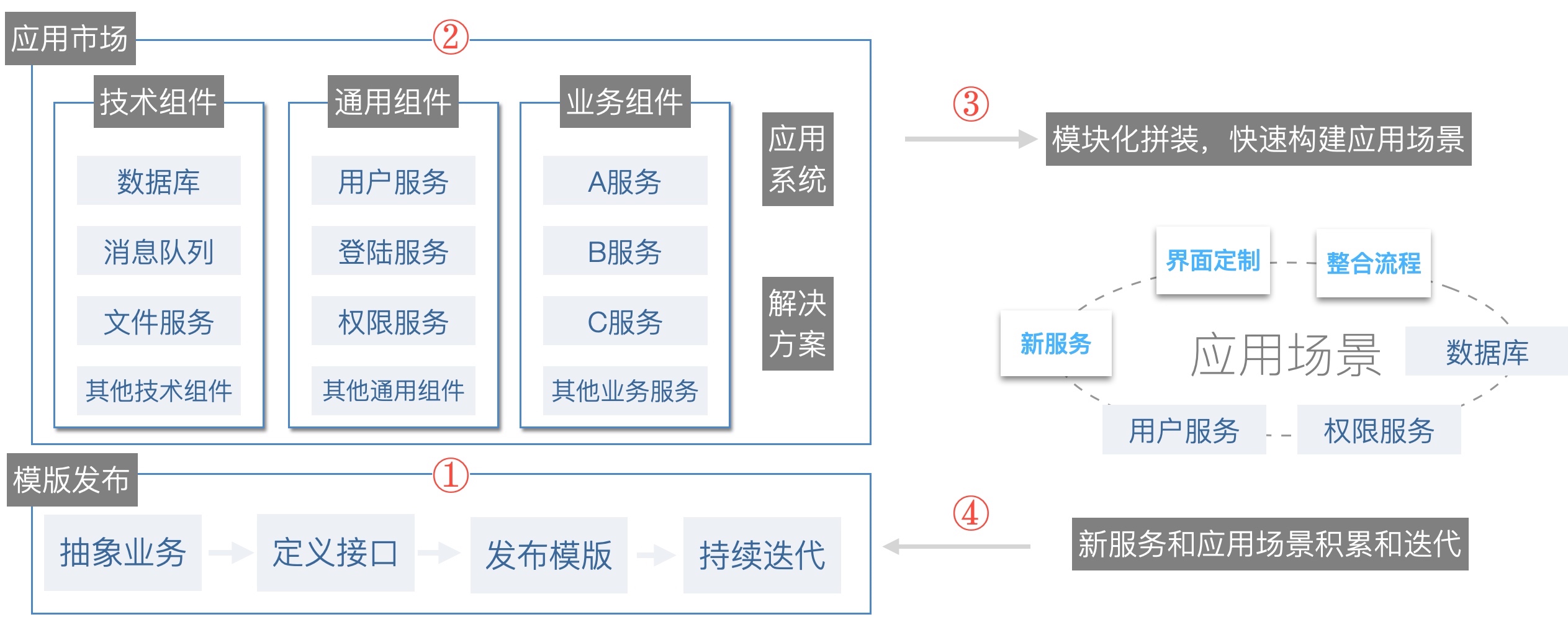
In Rainbond, the application template is the manifestation of the module, and the module release and assembly process is the release and assembly process of the application template.Module construction is a long-term process, emphasizing accumulation, and more of precipitation in the process of practice, and it needs to be continuously iterated based on feedback. This process is divided into four:
The first step: module is released in the form of application template with one click, what you see is what you get
To publish business components, you first need to define the granularity and business interface from a business perspective, and then build the components to be released in Rainbond. Rainbond supports variousbuild sources, andapplication templatesare also defined during construction. As long as the build is successful, you can One-click publishing into an application template means that any developer using the platform has the ability to publish an application template, and the low threshold for publishing is conducive to the sharing of knowledge and experience.
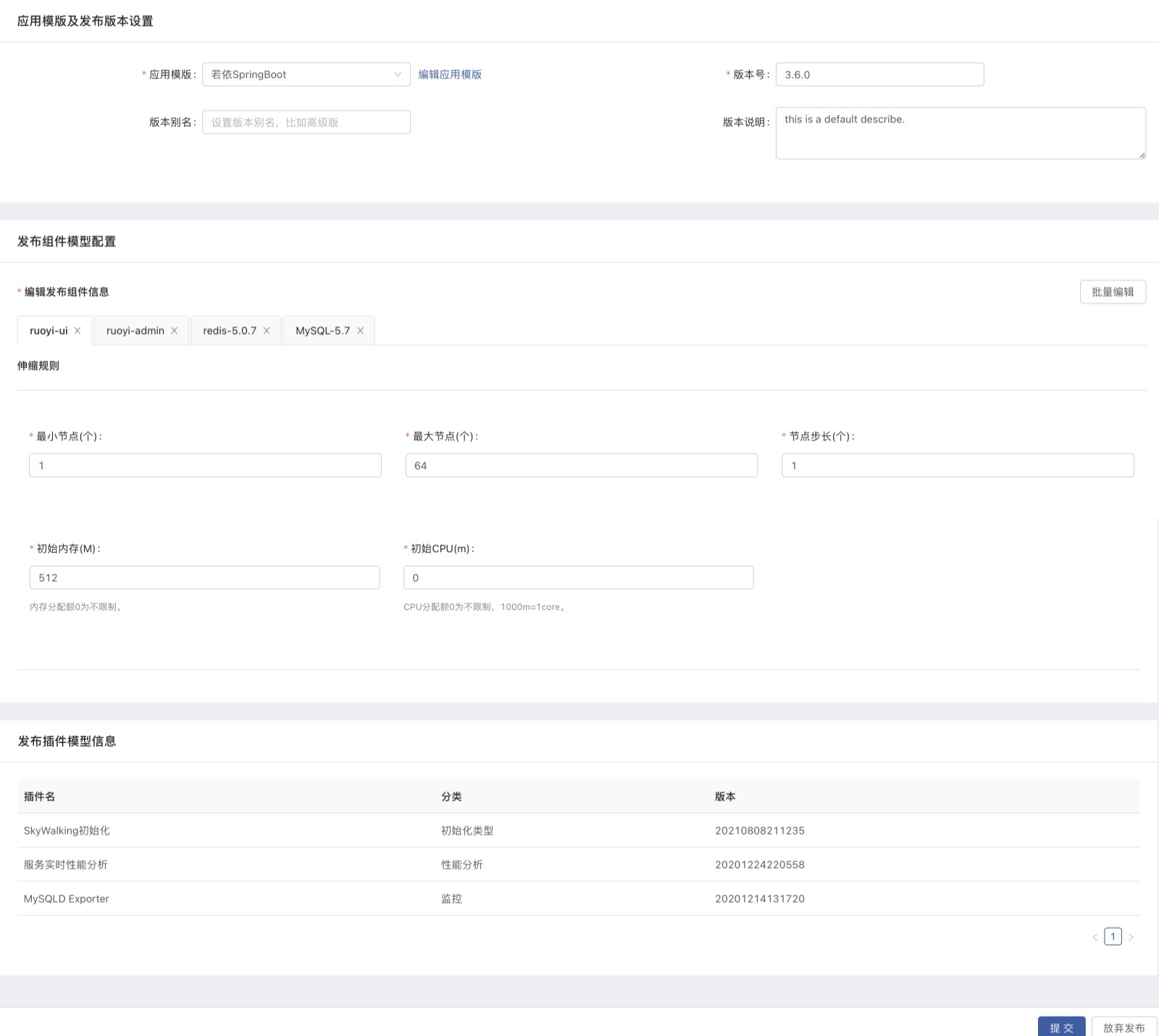
The second step: stores modules of different granularity through the application market
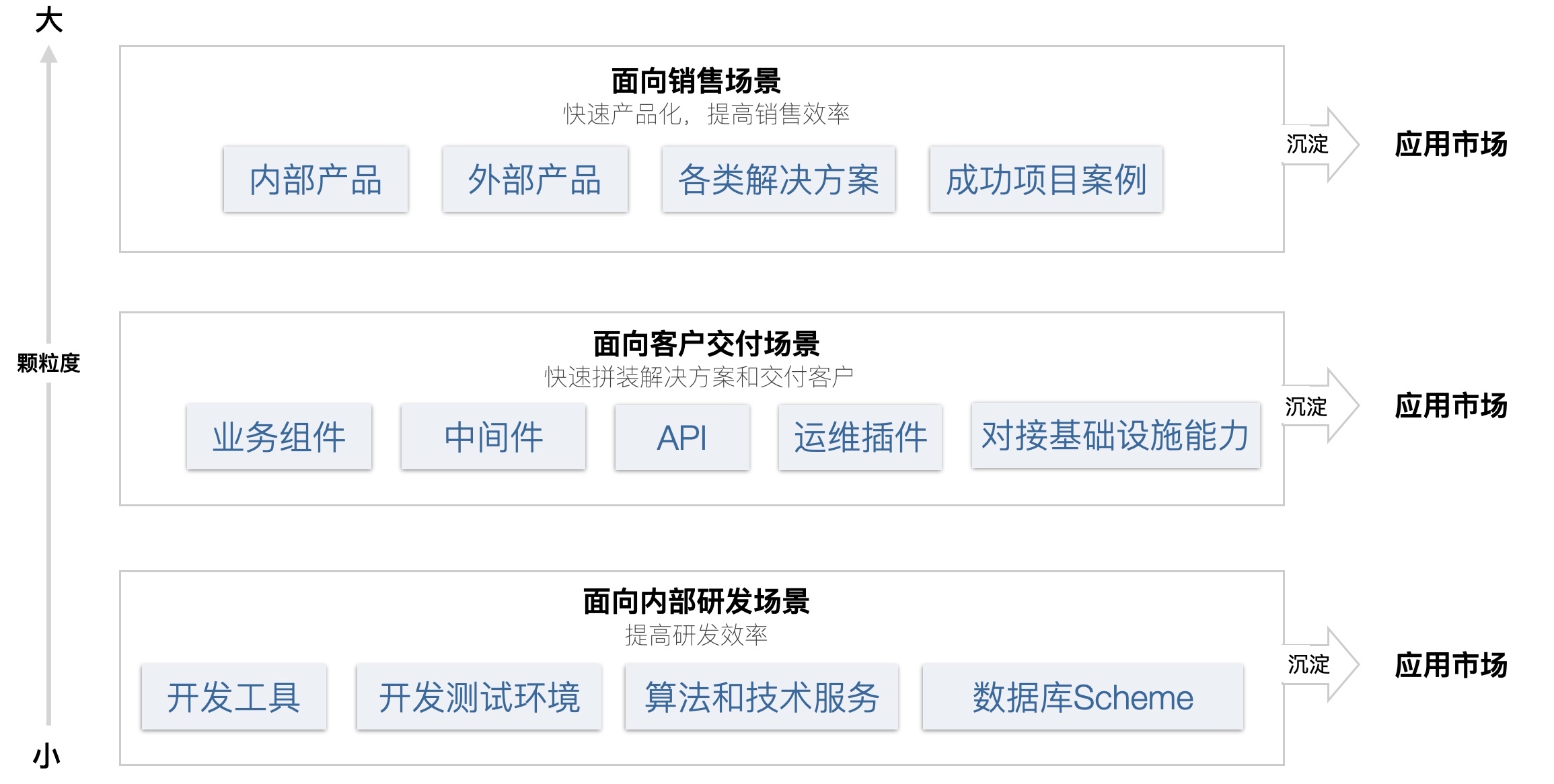
The application template supports different granularities, and different granularities are:for different usage scenarios.
- For internal R&D scenarios, it mainly accumulates technical templates, and the template granularity is relatively small, in order to improve development efficiency.
- For customer-oriented delivery scenarios, it mainly accumulates business templates. The templates have a large granularity. Through the templates, customer solutions can be quickly assembled to improve delivery efficiency.
- For sales scenarios, it mainly accumulates product templates that can be sold, with the largest granularity, which can help sales quickly demonstrate, use and deliver as a whole.
The third step:realizes modular assembly by applying templates
One-click installation of modules (application templates) that need to be assembled from the application market, and multiple modules can be assembled into the required scene through "drag and drop". After assembly, the original module will release a new version, and the assembled scene will be upgraded as needed.The newly assembled scene is released as an application template, which can be a larger module to support the assembly of a larger scene, and also realize the follow-up customer delivery process through the application template.
Fourth step:In real application scenarios, continuous accumulation and iteration
During the construction process of the module, it is necessary to avoid over-design and excessive disassembly in advance. The early disassembly of the module or the granularity of disassembly is too small, which will lead to high module development and maintenance costs and poor user experience.Therefore, the early design and development of modules can only account for a small part, and most modules can only see their value in real scenarios. At this time, they are released as reusable modules, which is more practical.At the same time, the boundaries and functions of modules are only meaningful in real scenarios, and need to be iterated continuously according to actual needs.
scenes to be used
Assemblable business modules to improve development efficiency and customer delivery speed
For the R&D and customer delivery scenarios of software companies, the assembleable business modules can be reused in the process of new project R&D and new customer delivery, reducing repetitive development and greatly improving efficiency.
Industry business middle platform to achieve industry capability accumulation and reuse
For industry users, in the process of digitalization, many systems will be built. These systems have many capabilities that are common. If these capabilities are accumulated, the subsequent construction process will be directly reused, which not only reduces the construction period, but also reuses mature capabilities. Improve system maturity.In addition, business integration and data integration scenarios are required, and the interconnection between systems can be realized through business orchestration.
Product packaging and modular sales for 2B software companies
For 2B software companies, they will face the contradiction between project personalization and product standardization. To solve this contradiction, there are two solutions.:is to allow personalized projects to quickly precipitate products. This process can be quickly achieved by publishing application templates. Realization; the other is to dismantle personalized projects in modules, different customers choose different modules, and realize personalized sales according to customer needs; these two schemes can be further integrated. In the early stage, personalized projects are the driving force, and the project’s Templates can be used as the product basis for demonstration and delivery to other customers. In the process of continuous delivery to customers, reusable modules and personalized modules are discovered and disassembled. The more customers are delivered, the more reusable modules are accumulated. The more you know which modules have commercial value, the more modularity becomes the foundation of the product, the better the service sales and delivery, the more mature the productization will be.