Offline Environment Software Delivery
Pain points of offline delivery
In traditional industries, such as government, energy, military, public security, industry, transportation and other industries, in order to prevent data leakage and operational security considerations, the network generally adopts the strategy of isolation between internal and external networks to prevent unnecessary risks. In terms of protection, network physical isolation is the most effective means of network security defense, and network isolation in the software delivery process will bring a series of delivery problems to external software developers and increase a lot of cost.e.g.:
1. On-site installation, deployment and acceptance testing are inefficient
During the delivery process, the application and all dependent resources need to be installed in the offline customer environment, and the customer environment may be various environments such as physical servers, virtual machines, private clouds, and K8s containers. This leads to inefficient installation and deployment in offline environments.Due to the complicated and error-prone installation and configuration process, it is necessary to redo the verification test work in the final delivery environment, which also wastes a lot of time.If the application system of the microservice architecture is deployed with higher complexity, the workload will be doubled.
2. Offline environment custom development and product upgrade, high cost
Custom development requires the input of developers, and the cost is inherently high. In the offline environment, it needs to be continuously iterated according to customer feedback, and the products are continuously upgraded during the iterative process. Every upgrade requires an installation, deployment and verification test process, which is very costly.If some work must be developed on site, the cost will be higher.
3. The network is blocked and cannot be operated remotely
After the delivery is completed, the application needs to be continuously operated and maintained to ensure the stability of the operation and the continuous availability of functions. In the case that the network cannot be connected, any problem needs to be arranged on-site to support, or even to arrange for the personnel to stay on site for a long time.
Technology selection
The root cause of the above problem is that the application system has more thanenvironment adaptation,application installation and deployment,application upgrade,application operation and maintenanceand other operations are not highly automated, requiring a large number of manual operations, so the efficiency is very high Low, problem solving focuses on solving application management automation.At present, cloud native technology has become more and more mature, and cloud native technology mainly solves the problem of automation of application management. There are two kinds of open source implementation solutions :
1. Rancher+Helm
Rancher is a K8s management tool. It provides K8s management UI and uses Helm for package management.Corresponding to the problem of offline delivery, Rancher can be installed in a variety of operating environments (physical servers, virtual machines, private clouds), and provides automatic operation and maintenance functions for some applications, which can solve the problems of adaptation and application operation and maintenancein more than environments , while <code>application installation and deploymentand application upgradeproblems can be solved by Helm package.
2. Rainbond+ Application Template
Rainbond is an "application-centric" application management platform. Application templates are Rainbond's solution for packaging applications. Rainbond provides full lifecycle management of applications (application development, application orchestration, application delivery, and application operation and maintenance).Rainbond can be deployed to various operating environments (physical servers, virtual machines, private clouds), and can also be deployed to existing K8s clusters and Ranchar to solve the problem of customermulti-environment adaptation; Rainbond provides application operation and maintenance panels to solveApplication operation and maintenanceissues are relatively simple to use and do not need to understand the concept of containers; Rainbond's application template is a bright spot, as long as the application running on Rainbond can be published as an application template with one click, which simplifies the production of application templates, and the application The template can export offline packages, which is especially suitable for application installation and deploymentand applicationin offline environment.
Let's compare the two options
The biggest advantage of Rainbond compared to Rancher is its ease of use. It does not need to learn K8s and container-related technologies and concepts. In addition, the integrated development environment and module arrangement functions provided by Rainbond can greatly improve the efficiency of custom development.The biggest advantage of Rancher is that it is fully compatible with the K8s system. If you understand K8s, you can get started quickly.
Comparison of Helm and application templates
| Contrast | Helm | application template |
|---|---|---|
| Install and upgrade | few configuration | Fully automatic |
| Production process | Manually written | Fully automatic |
| Export and import offline packages | not support | support |
| Configuration adjustment | Supports predefined configuration tweaks | support |
| Module customization | not support | support |
| Compatible with other K8s versions | compatible | Requires pre-installation of Rainbond |
Rainbond's application template is completely consistent with OAM's design concept. The "application-centric" design concept shields the complexity and differences of container infrastructure, and brings low mental burden, standardization, and consistency to platform users. application management and delivery experience.
In a comprehensive comparison, in the offline delivery scenario, the Rainbond+ application template has obvious advantages. Let's combine practical examples to explain the entire process of delivering the Rainbond+ application template to offline customers.
Offline application delivery using Rainbond application templates
For application delivery in an offline environment based on**, you only need to publish the business developed in the development environment to the application market, export the offline package of the application template based on the application market, and import it in the delivery environment. Install**to run automatically.
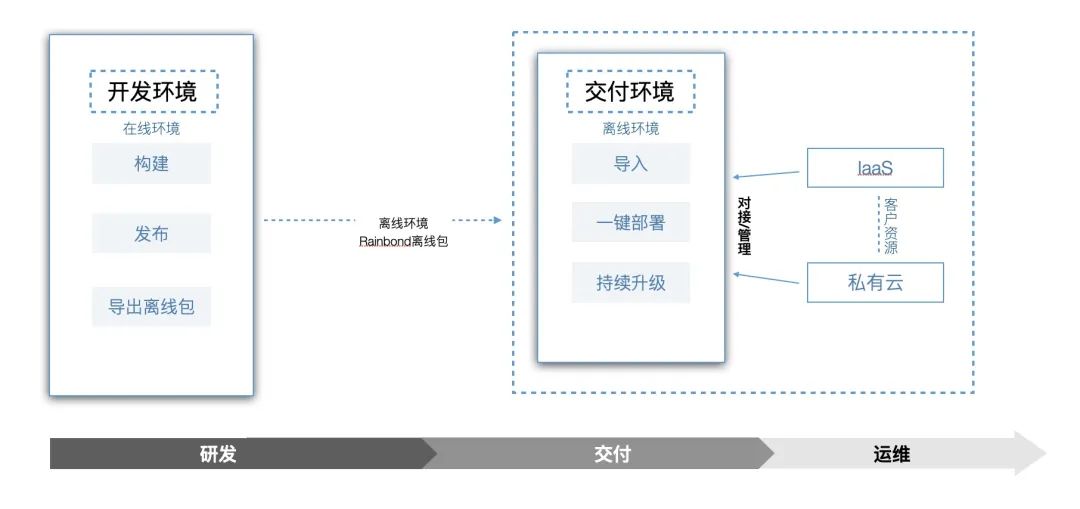
Prepare the environment in advance
-
It has two sets of Rainbond clusters, simulating the development environment and the delivery environment (the development environment is an online environment, and the delivery environment is an offline environment).
-
For development environment installation, refer to Online Installationdocument;
-
For installation in the delivery environment, refer to the document Offline Installation;
-
Have U disk, CD and other offline environment application template offline package transmission media.
1. Business deployment
The whole process starts with the development environment, and we first need to move the business to Rainbond.In the development environment, based on the deployment of your own business, you can support source code or mirroring.Currently taking Spring Cloud microservice framework Pig as an example, deployment referenceSpring Cloud Pig deployment and application production in Rainbond.
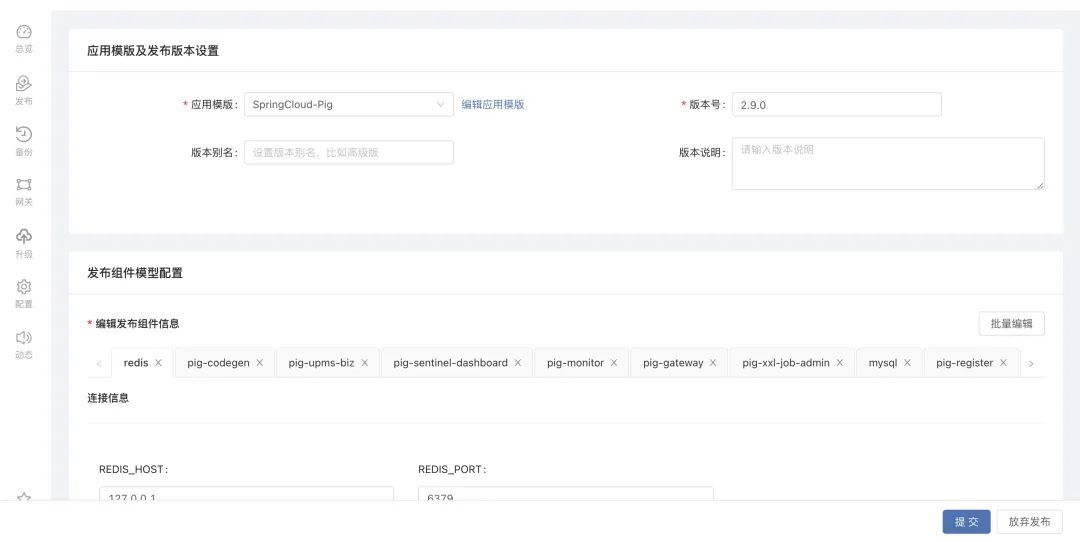
2. Application release
Publish the application that has been developed in the development and testing environment to the internal component library:Click the button Publish in the left navigation bar of the application, and select to publish to the component library This process requires to create a new application templateThe application template defines the following information:
| option name | illustrate |
|---|---|
| name | Define application name (required) |
| Scope of release | The visible scope of the application template,**is visible to the current team,**is visible to the current team,is visible to all teams, andis visible to all teams (required) |
| Category labels | Application tags, which can be categorized by architecture, industry, and deployment method |
| Introduction | App description to help users understand the app |
| Logo | App logo image |
Define app release version:after creating app template
| option name | illustrate |
|---|---|
| version number | When the same application is released multiple times, if the version number is the same, the released version will be overwritten. If different, it will be released as a new version. When the application is upgraded or rolled back, the platform will judge according to the version (required) |
| version alias | App aliases, e.g. Premium, Junior |
| Imprint | The description of the current release version, which can distinguish the functional differences of different versions and other information |
publish component model configuration:
| option name | illustrate |
|---|---|
| connection information | When password information appears in the connection information, you can choose to automatically generate a random value every time you deploy |
| environment variable | Edit the default environment variables for this component |
| Scaling rules | Define the maximum and minimum number of nodes that the component can scale, the node scaling step, and the minimum installed memory limit. |
Publish plugin model info:
When the component of the application to be published carries a plug-in, it will be displayed and published along with the component during the publishing process.
After all the information is configured, click thereleasebutton to publish, and the dependencies between components, environment configuration, persistent storage, plug-ins, operating environment and all the above-defined information defined in the business development process will be packaged and released.
3. Application export
Export the application template locally, find the published application in the homepageapplication market, click the last buttonto expand, selectto export the application template, select the application version and click theapplication template specificationExport button , the export process is fully automated. After the export is complete, click thedownloadbuttons to download the application template to the local, save it to a mobile storage device such as a U disk, and bring it to the offline delivery environment.
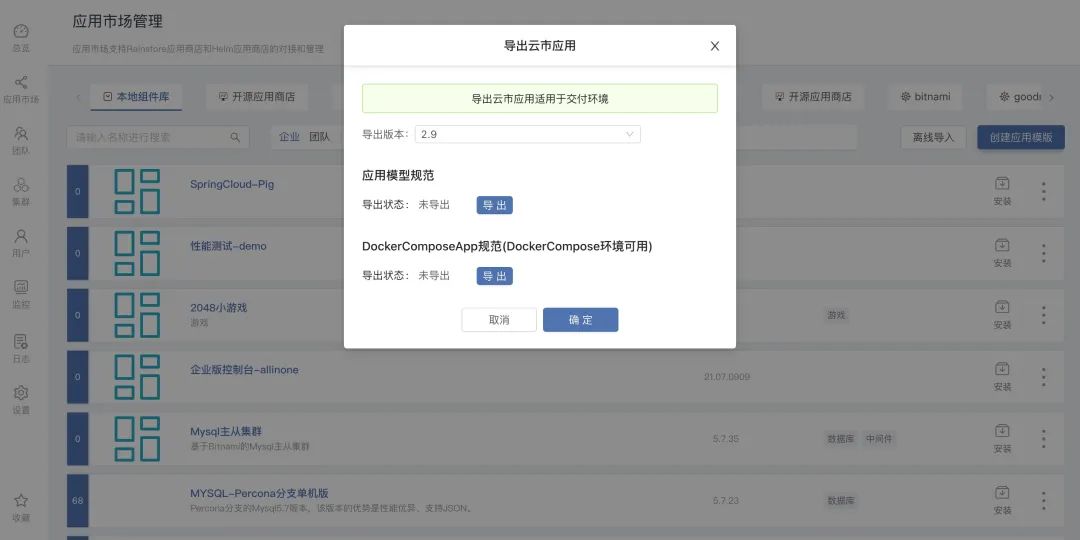
Next, the offline delivery process is entered. The delivery personnel carry mobile storage devices such as U disks with offline packages and start importing application templates.
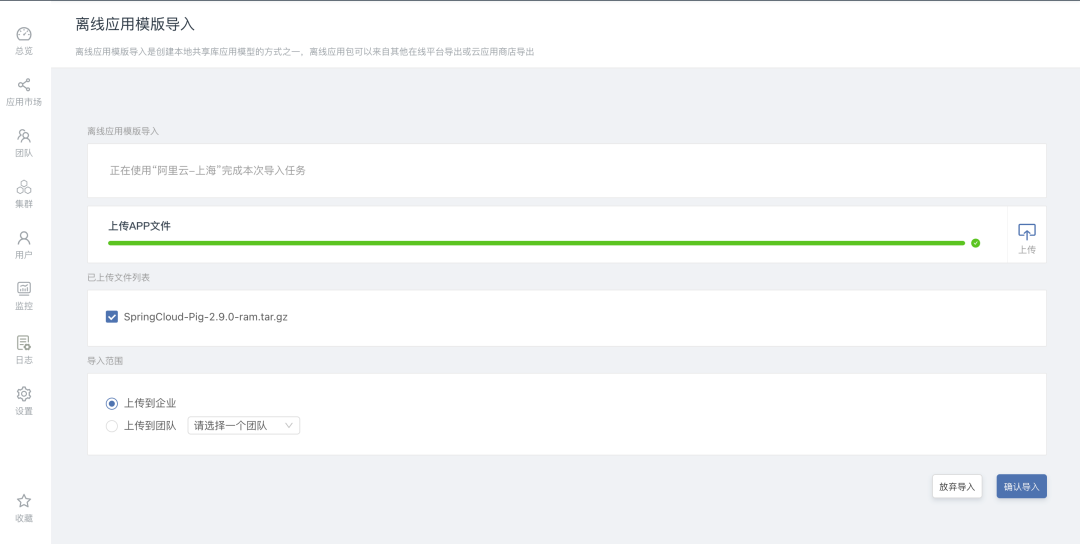
4. Application Import
Use the exported application template to import in the delivery environment, click theoffline import buttonon the application market interface, select the local application template to upload, and after uploading, selectto import the scope: Enterprise or team, the enterprise is the owner of the current delivery environment It can be seen that the team is visible to the people under the designated team; clickto confirm the import andto enter the automatic import step.
5. One-click deployment
After the application is imported, click theinstallbutton to deploy the business system in the current delivery environment with one click. The business operating environment of this environment is exactly the same as the development environment. At this point, the software delivery in the offline environment is completed.
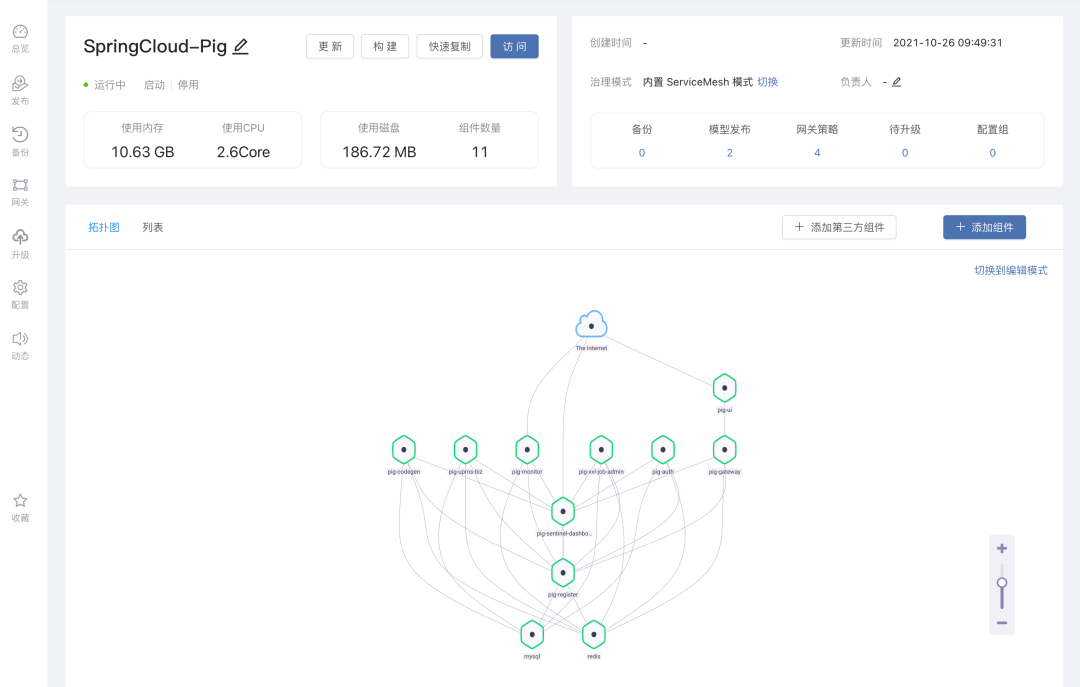
6. Incremental upgrade
Some modules need to be upgraded in the software update iteration process. During such an upgrade, incremental upgrade can be used to save publishing, import and export time.
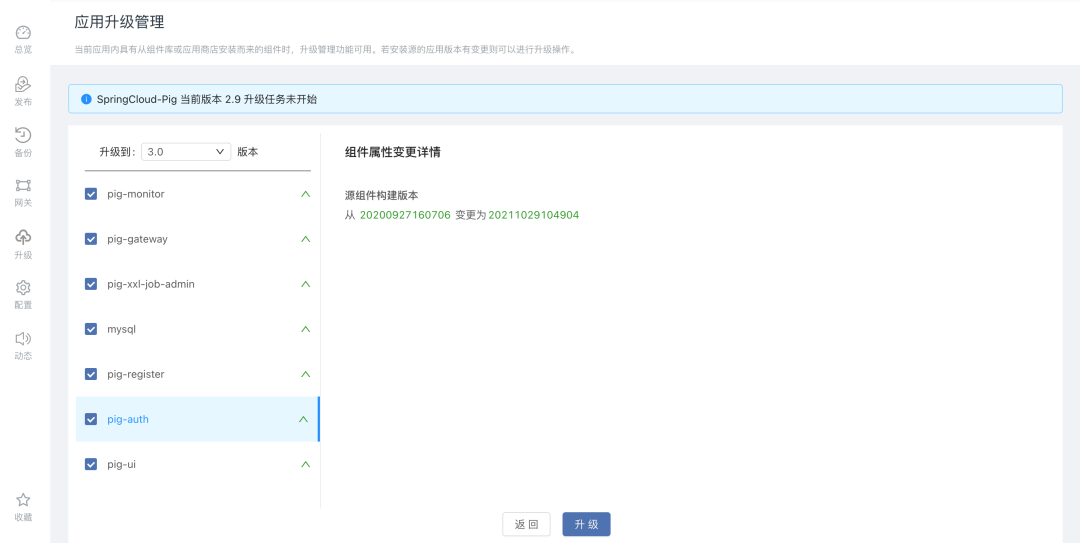
To achieve the effect of incremental upgrade, you need to perform theapplication releaseoperation again, select the previously created application template, and modify the version number. If the previous version is set to 2.9, this release is set to 3.0.
In theapplication releasestep, the components that need to be upgraded are selected for release, and it is not necessary to select all components.After the release is complete, export the offline package of the new version of the application template and import it again in the delivery environment.
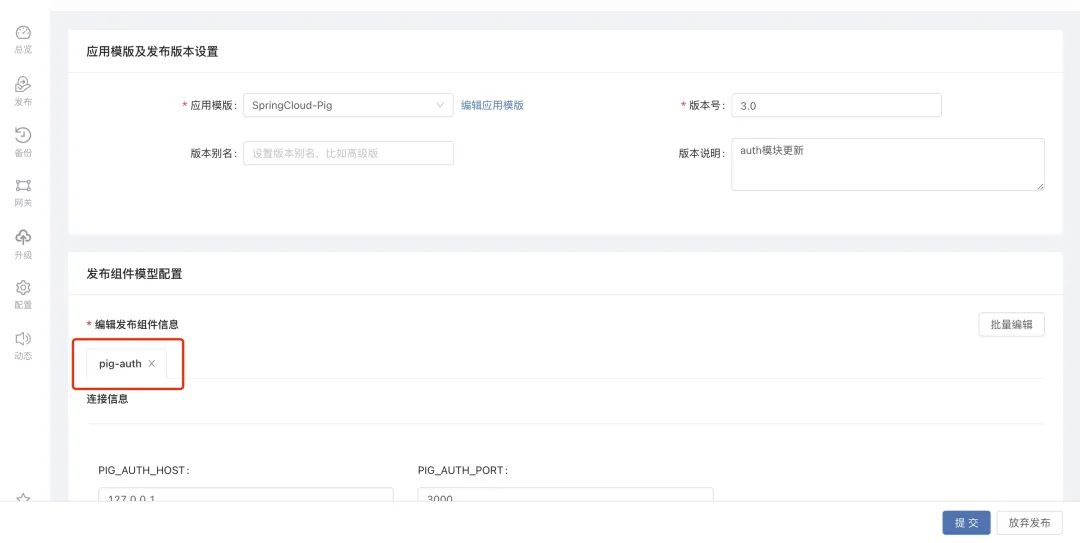
After the delivery environment is imported, the platform will compare the different versions of the application template, and prompt the user to upgrade through theto be upgraded optionin the application topology diagram.Display the property changes between versions. Users can select the version that needs to be upgraded to upgrade. The platform will automatically perform the upgrade operation and change the component build version.
The environment configuration information will not be changed during the upgrade process. This kind of information needs to be changed manually to take effect.:
-
the value of the environment variable
-
Contents of the configuration file
-
persistent storage
7. One-click rollback
When an exception occurs and needs to be rolled back after the upgrade version goes online, the platform provides a one-click rollback function. Select the corresponding record on theupgrade recordinterface and click therollbackbutton to roll back the upgrade operation.
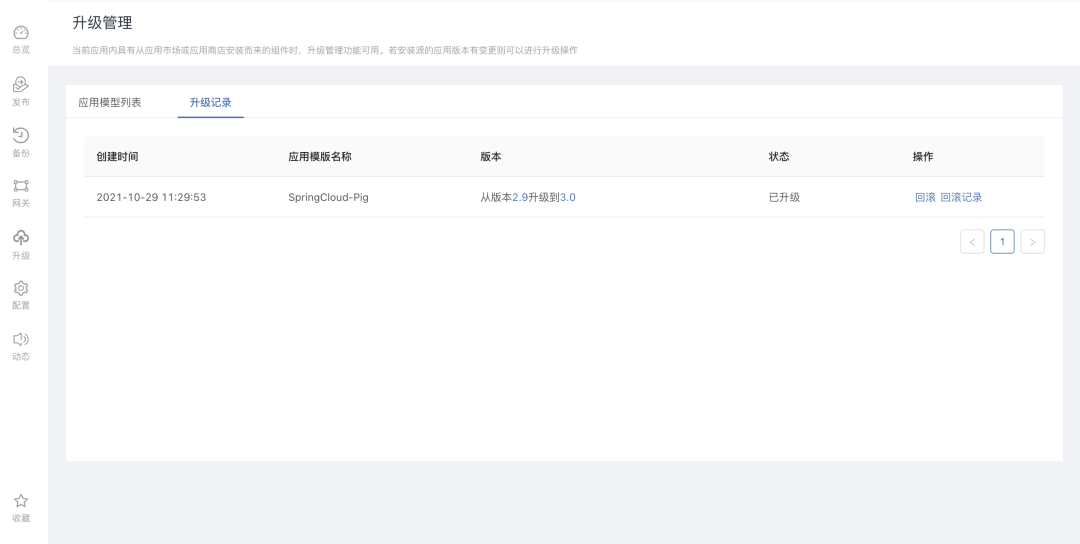
During the rollback process, the newly added components will not be deleted, and manual operations are required to make changes.
8. Application operation and maintenance functions
After the software product is delivered, it needs to carry out long-term operation and maintenance. At the operation and maintenance level, the delivery personnel need to consider the availability, scalability, and resource monitoring of the service. Rainbond provides many operation and maintenance functions, such as:
- Service performance analysis
The performance analysis function is extended through the Rainbond plug-in mechanism. The service real-time performance analysis plug-in runs in the same network space as the target analysis service. It monitors the traffic of the network card to statistically analyze the work performance of the service. It has no effect on the work process and performance of the service itself. The average response time, throughput and other main indicators.
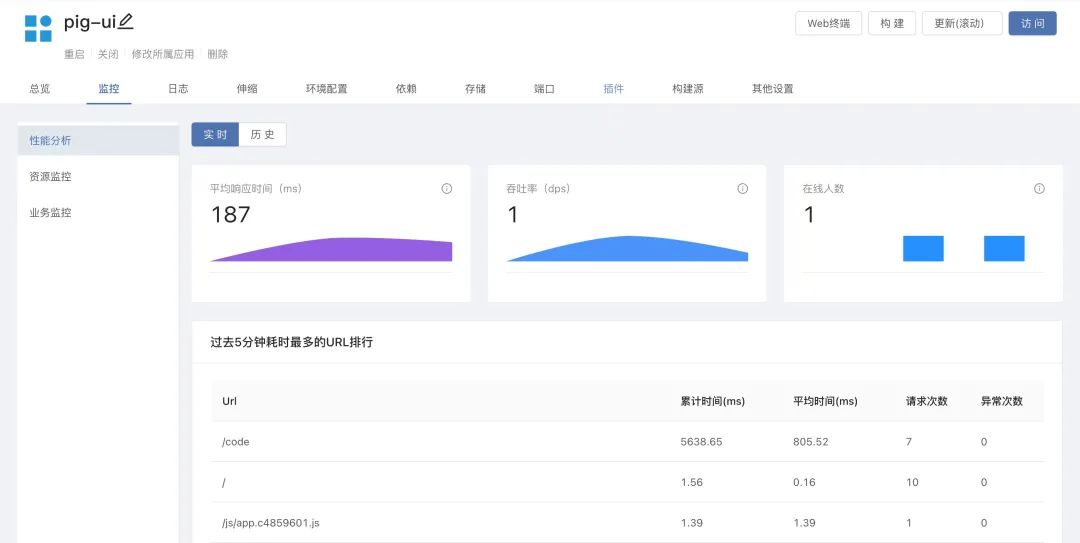
-
Resource monitoring alarm
Monitor the platform and business based on Prometheus, dynamically discover targets to be monitored based on ETCD, and automatically configure and manage Prometheus services.
-
instance scaling
Scale service components vertically or horizontally, and flexibly expand capacity during peak traffic periods.
-
Gateway management
Application Gateway supports grayscale publishing and A/B testing functions.
scene expansion
The above examples are mainly for common offline software delivery scenarios, but in real offline delivery scenarios, the following scenarios may also exist, such as:
-
Offline module customization, the modules delivered by each customer are not necessarily, and the modules can be turned on or off on the customer site according to the needs, or the modules are arranged.
-
Offline custom development, complete software development process in offline scenarios, including source code management, source code compilation, development and testing environment management, team collaboration, version release process, etc.
Summarize
In this paper, we analyze the problems of offline delivery scenarios, compare possible technical solutions, and use an example to fully explain the entire offline delivery process, which is highly automated.Using Rainbond for offline delivery can definitely improve efficiency, but in what ways can we improve our efficiency, let me summarize:
-
One-click export and import of offline environment application system During the delivery process, you only need to import the offline package of the application template based on Rainbond export in the delivery environment, and then you can install the entire business system with one click.
-
The development environment and the offline environment are exactly the same. shields the differences in the underlying environment and delivers based on the application template. The template packages the running environment and dependencies of the application. The development environment and the offline environment are exactly the same, and no repetitive testing is required.
-
Integrated customer customization environment During the software delivery process, different customers will have different customization requirements, which means that different modules need to be developed for different customers. These customized modules are different in different projects, and are provided by Rainbond. If you need to customize the development, you can directly perform offline code development work based on the Rainbond deployed in the delivery environment, including source code compilation, configuration component running environment, etc., in the delivery environment All customization work is done in .
-
Offline environment customer continuous delivery For the project implementation team, new functions and defect fixes need to be quickly implemented into the delivery environment or users during the implementation process. In the traditional continuous delivery process, delivery personnel need to be stationed in the offline environment. , manually perform the update and online operation, this process not only increases the delivery time, but also increases the risk of deployment if the long-term manual operation is performed; and the continuous delivery capability of Rainbond can realize the subsequentincremental import, export and version upgrade of the application, Can bring the following advantages:
-
This is achieved through automation, effectively shortening the time from code submission to deployment and launch.
-
Software is in a state of deployable upgrades throughout its lifecycle.
-
Simplify the upgrade steps and make the software version clearer.
-
Make the delivery process a predictable, visual process.
-
-
Automated operation and maintenance in offline environment
Service high availability, self-fault-tolerant and self-recovery mechanisms, reduce manual operation and maintenance, and improve business system stability.