Envoy fuse current limiting practice (2) Rainbond based on RLS service full current limiting
Envoy can be used as a proxy implementation in the Service Mesh microservice framework. The built-in microservice framework of Rainbond is also implemented based on Envoy.The circuit breaker practice described in this article is implemented based on Rainbond's unique plug-in mechanism.
Envoy speed limit
While distributed circuit breakers are very effective in controlling throughput in a distributed system in most cases, sometimes it doesn't work very well and full throttle is required.The most common case is when a large number of hosts are forwarding to a small number of hosts and the average request latency is low (eg connections/requests to a database server).If the target host becomes the standby host, the downstream host will overwhelm the upstream cluster.In this case, it is difficult to configure each downstream host with sufficiently strict fuses so that the system can operate smoothly, while still preventing cascading failures when the system starts to fail.For this situation, a full throttle is a good solution.
The Envoy global rate limit solution needs to be implemented based on a global RLS (rate limit service) service. RLS is designed as a Go/gRPC service that provides different rate limit scenarios for different types of applications.
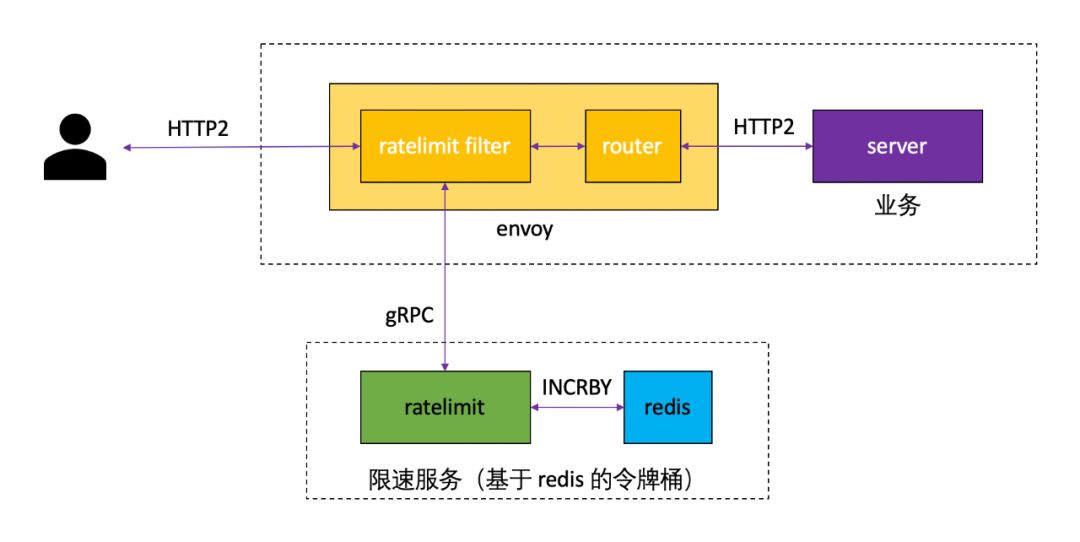
Build a global speed limit service
An out-of-the-box full rate limiting service has been incorporated into Rainbond's built-in open source app store, and users can install rate limiting services with one click based on the following operations.
- Access to the built-in open source app store
Select the app market tab on the left, switch to the open source app store tab on the page, and search for the keyword rate limit** to find the rate limiting service.
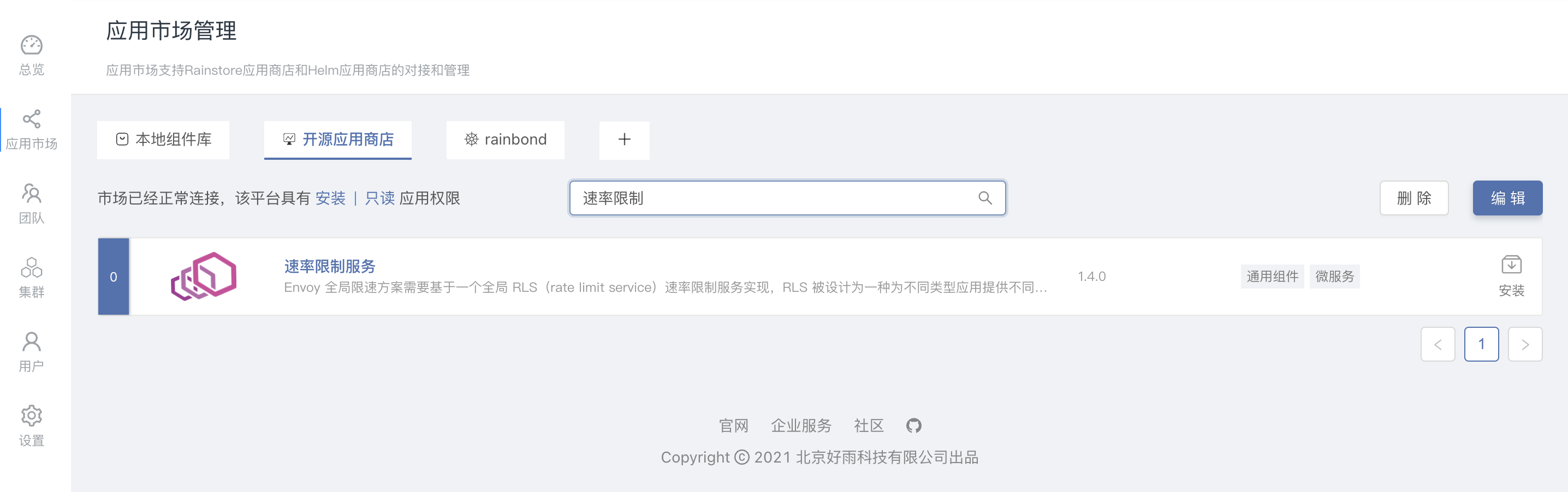
- A key installation
Click to install on the right side of the rate limiting service to enter the installation page. After filling in the simple information, click to confirm to start the installation, and the page automatically jumps to the topology view.
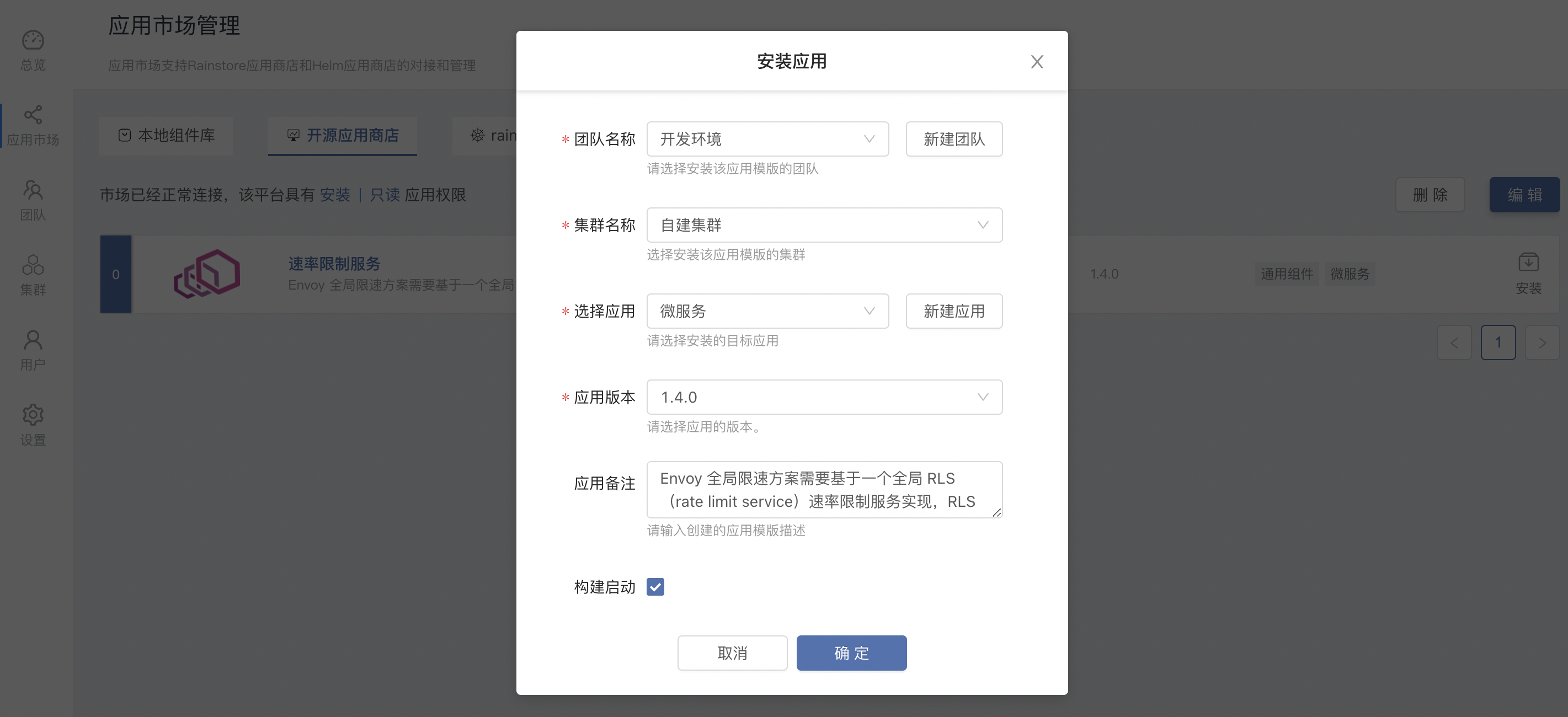
parameter description:
| options | illustrate |
|---|---|
| Team Name | User-created workspace, isolated by namespace |
| cluster name | Choose which K8s cluster the rate limiting service is deployed to |
| Choose an application | Choose which application the rate limiting service will be deployed to. The application contains several related components |
| App version | Select the version of the rate limiting service, the current version is 1.4.0 |
After a few minutes, the rate limiting service will be installed and running.
Full speed limit configuration
The global rate limit can be configured by editing the configuration file /data/ratelimit/config/config.yamlin the Rate-limit-service component.
The default configuration content is as follows:
domain: limit.common
descriptors:
- key: remote_address
rate_limit:
unit: second
requests_per_unit: 10
# Black list IP
- key: remote_address
value: 50.0.0.5
rate_limit:
unit: second
requests_per_unit: 0
In this section of configuration, a rate limit configuration that allows 10 requests per second to pass through for domain name domain is defined.
For the case where the client IP is 50.0.0.5 , the speed limit configuration that allows 0 requests per second to pass through is implemented, which can be understood as a blacklist configuration by users.
More configuration examples can be found on GitHub - /ratelimit: Go/gRPC service designed to enable generic rate limit scenarios from different types of applications.
Citing a global speed limit service
The service components that need to be speed-limited need to meet the following conditions:
-
Install and configure service integrated network management plugin
-
Dependency
Rate-limit-service
Rainbond expands the operation and maintenance capabilities of the business through the plug-in mechanism. By installing the -service integrated network management plug-in , the management capabilities can be expanded at the network entrance of the speed-limited business.Service integrated network management plug-in essentially expands the capabilities of Envoy, and realizes the full speed limit function by calling Rate-limit-service.
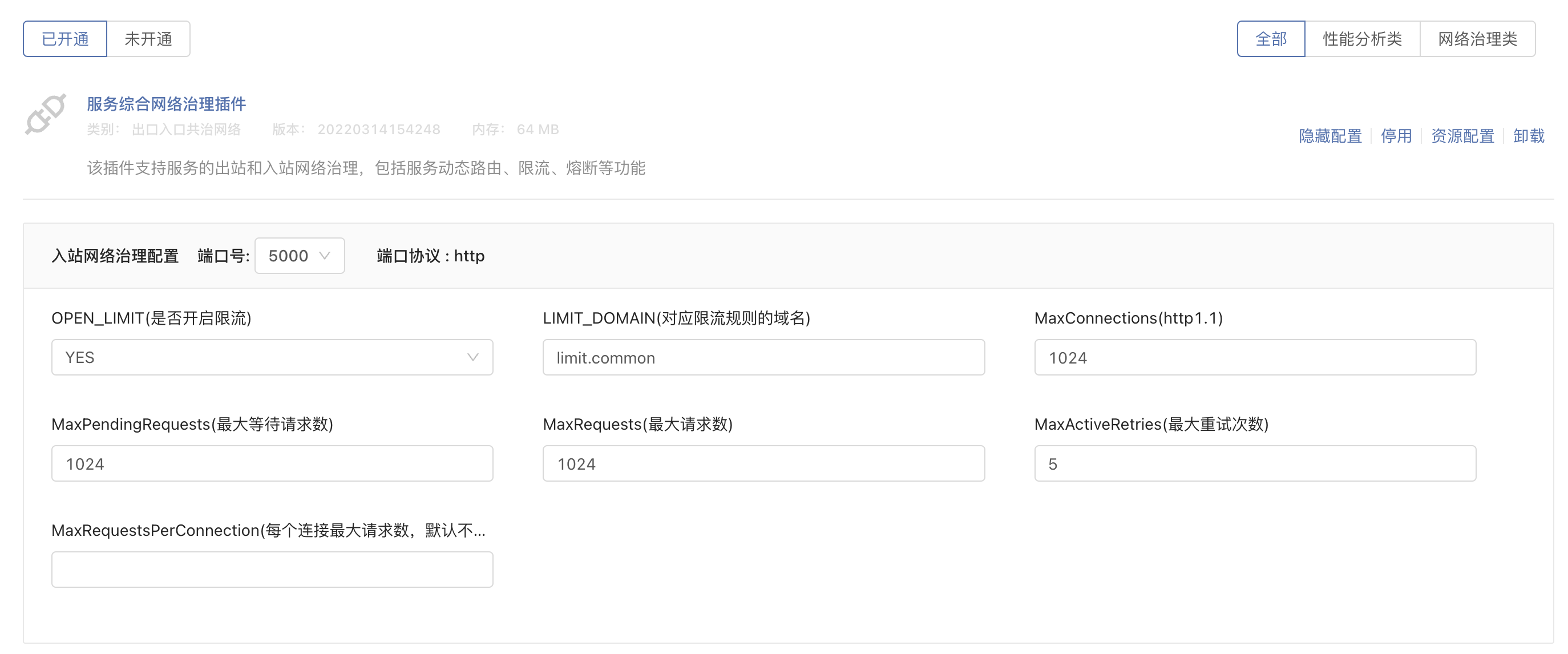
Make sure that OPEN_LIMIT (whether to enable current limiting) option is YES, LIMIT_DOMAIN (domain name corresponding to the current limiting rule) is consistent with domian in the full current limiting configuration above.So far, the configuration on the side of the speed-limited service is completed.
verify
In order to verify whether the speed limit takes effect, the Locust stress test toolis introduced to continuously generate access requests to the speed-limited services.
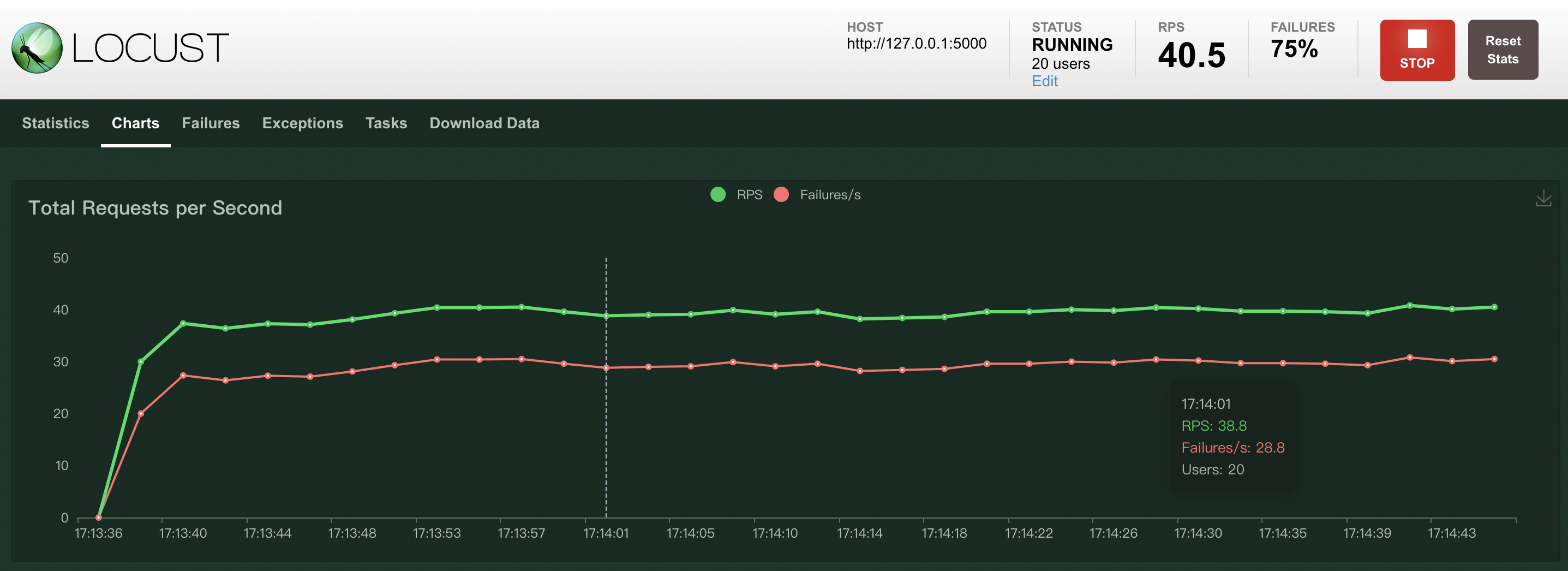
After the default global speed limit policy is applied, about 74% of the total number of accesses is limited by the speed-limited business at 40 RPS.
Access denied, get a 429 return code, and prompt Too Many Requests, which is the standard return mode for service rate limiting.
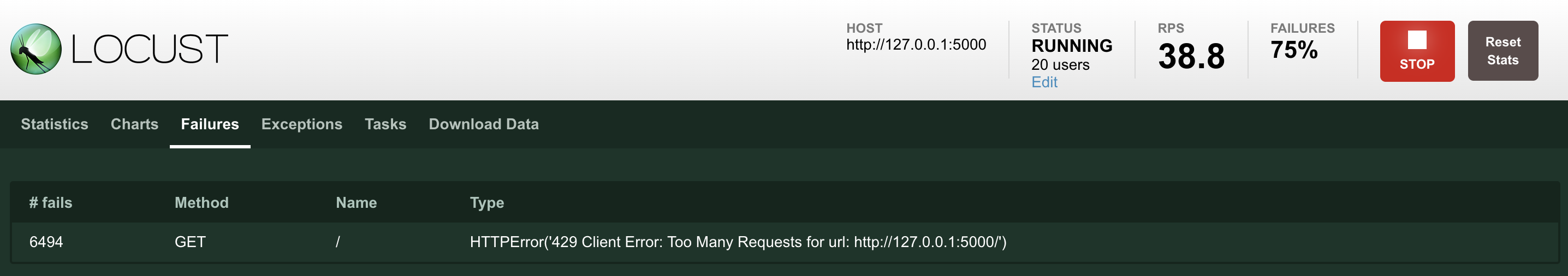
The -service integrated network management plug-in installed by the speed-limited service supports dynamic configuration.This means that without stopping the service, you only need to set the OPEN_LIMIT (whether to turn on the current limit) option to NO and update the configuration, the service speed limit can be turned off, and the number of access errors will drop to 0.
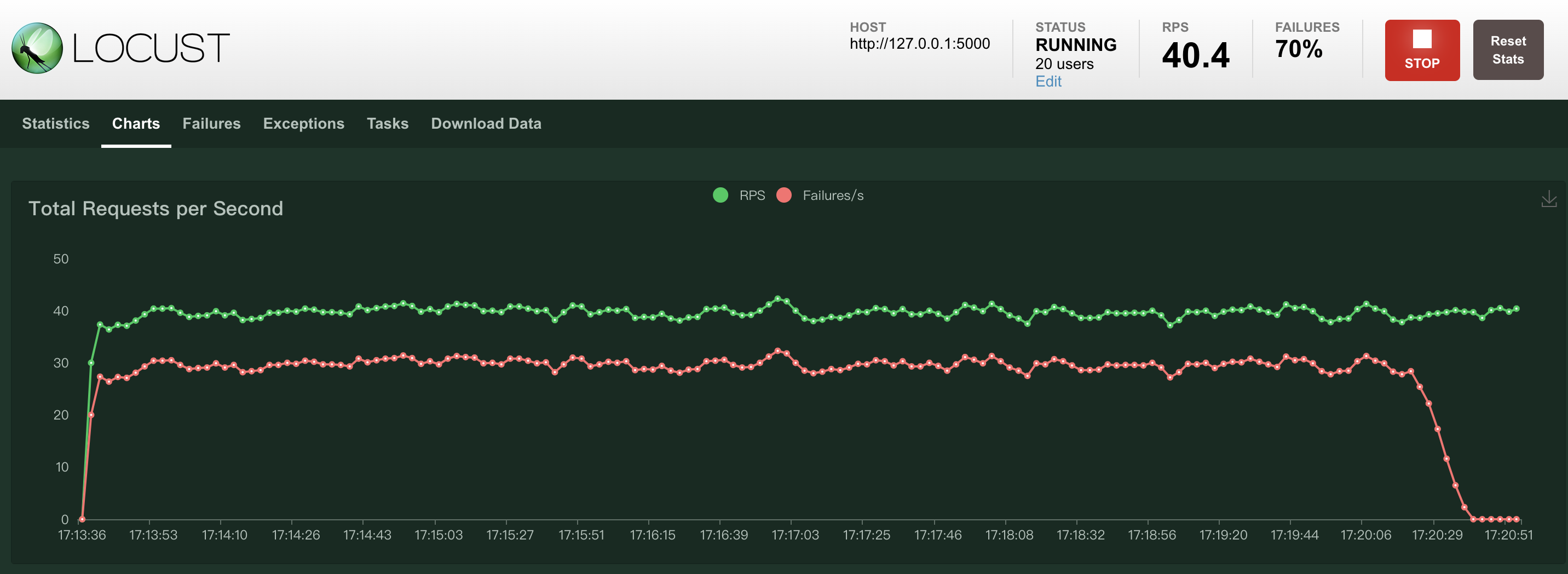
The full speed limit takes effect on the network entry of the speed-limited business, which means that no matter the request comes from other microservice components deployed by Rainbond or from external access outside the gateway, the request will be speed-limited.
Summarize
The full speed limit is an effective way to protect microservices in sudden traffic surge scenarios. The built-in microservice framework of Rainbond supports the Envoy service speed limit scheme that complies with the RLS specification.The configuration is very simple and supports dynamic changes. The examples in this article strive to show you the configuration practice of the full speed limit in the Rainbond system in an intuitive way.