Use Nocalhost to develop microservice applications on Rainbond
This article will introduce how to use Nocalhost to quickly develop the development process and practical steps of microservice applications on Rainbond.
Nocalhost can directly develop applications in Kubernetes, and Rainbond can quickly deploy microservice projects without writing Yaml. Nocalhost combined with Rainbond accelerates our microservice development efficiency.
1. Introduction
Nocalhost is an open source IDE-based cloud native application development tool:
- Build, test, and debug applications directly in a Kubernetes cluster
- Provides an easy-to-use IDE plugin (supports VS Code and JetBrains), and Nocalhost maintains the same development experience as local development even when developing and debugging in a Kubernetes cluster
- Develop with Instant File Sync: Instantly sync your code changes to remote containers without rebuilding images or restarting containers.
Rainbond is a cloud-native application management platform:
- It is easy to use, does not need to understand containers, Kubernetes and the underlying complex technologies, supports the management of multiple Kubernetes clusters, and manages the entire life cycle of enterprise applications.The main functions include application development environment, application market, microservice architecture, application delivery, application operation and maintenance, application-level multi-cloud management, etc.
2. Local + Rainbond development of microservices
In the past, when we developed microservices locally + Rainbond, we ran the modules to be developed locally, and other modules ran on Rainbond. We communicated and debugged locally through the Rainbond gateway.
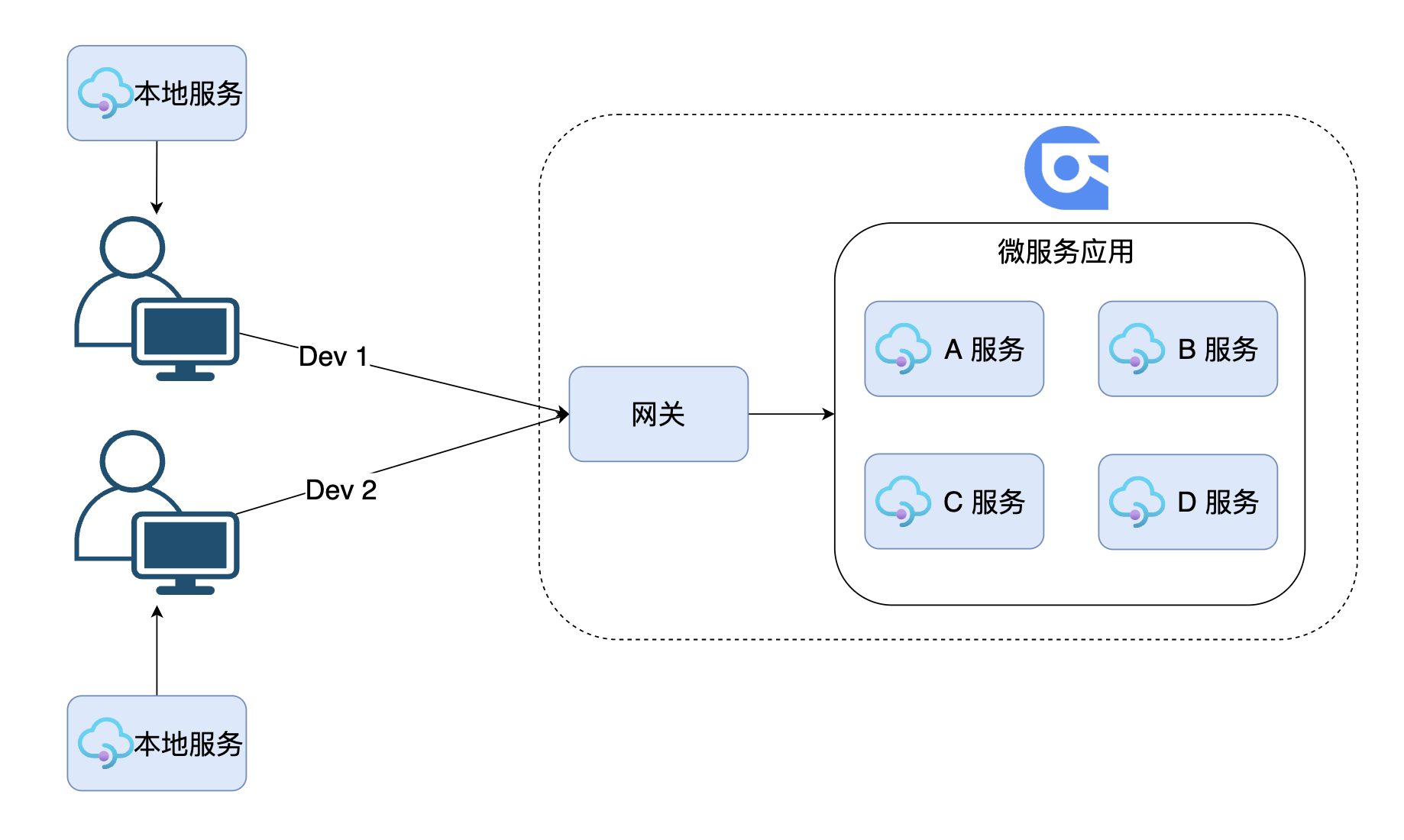
This will encounter some problems:
- Difficulty in multi-person collaborative development and joint debugging
- local environment differentiation
- Cannot call other microservices through the registry (Nacos)
- Remote debugging is difficult
- Limited to local resources
3. Use Nocalhost + Rainbond to develop microservices
Now when we develop microservices through Nocalhost + Rainbond, all services run on Rainbond. When developing, the local Vscode is directly connected to the Rainbond component, and is synchronized with the local code to the Rainbond component in real time.When multiple people develop joint debugging, they can conduct joint debugging between services through the built-in Service Mesh of Rainbond.
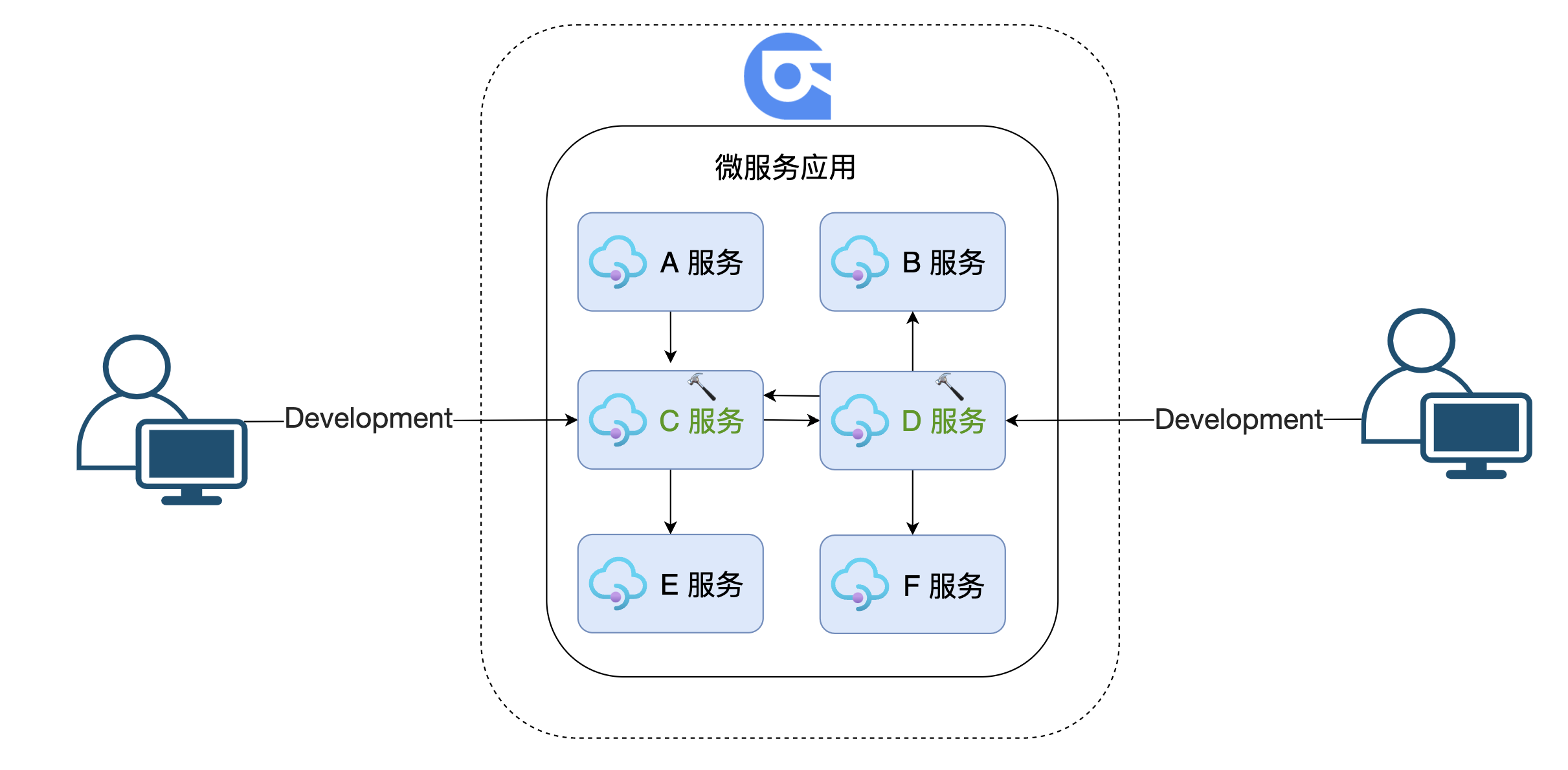
Using:to develop, you can solve the problems encountered in local development0
- Multi-person joint debugging and development are more convenient
- Services all run on Rainbond, no longer limited to local
- closer to production
- Remote Debug
- Call other microservice components through the registry (Nacos)
4. Practical steps
Nocalhost currently supports two development:
- Repliace DevMode
- Duplicate DevMode
This article will mainly introduce Replace DevMode. When entering Replace DevMode, Nocalhost will perform the following operations on the component:
-
Reduce the number of copies to 1
-
Replace the container's image with a development image
-
Add a sidecar container.
-
Forward a local port to the file sync server.
-
Start the local file sync client.
-
Open a remote terminal.
4.1 Install Nocalhost plugin
Nocalhost supports VScode JetBrains, here we mainly introduce VScode plugin installationrefer to the official website documentation.
- Open VScode, click the
Extensionbutton icon on the left
icon on the left - Enter
Nocalhostin the search box, selectNocalhost plugin, and click the Install button
4.2 Install Rainbond
We choose to install Rainbondbased on the host
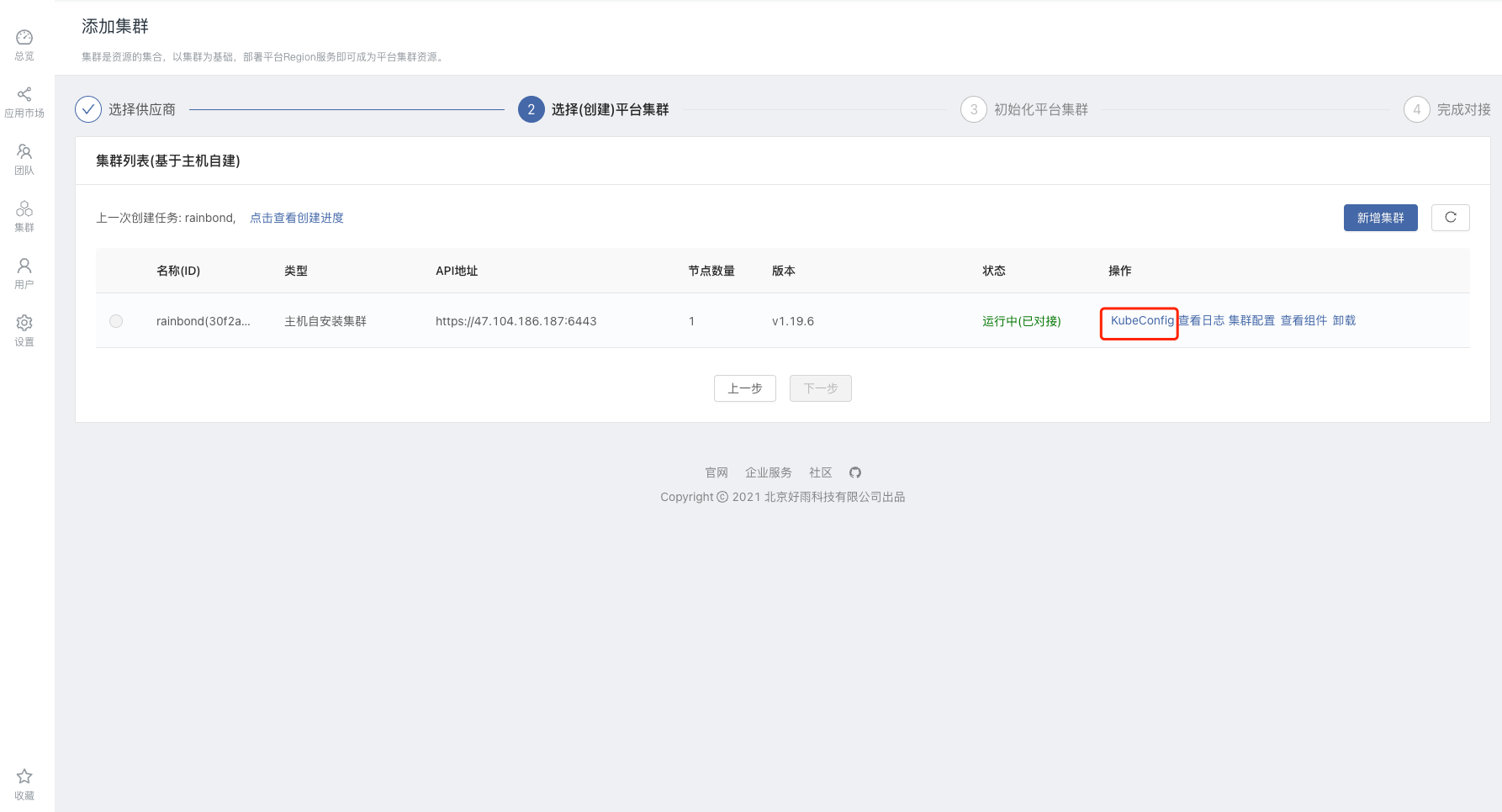
4.3 Nocalhost docking with Rainbond cluster
- Get
kubeconfigfile, enter the Rainbond cluster view -> click on node configuration -> kubeconfig
-
We copy
kubeconfigfiles to local and save asyamlfiles. -
Open Vscode, click button
, open the Nocalhost plugin, select Connect to Cluster, select the path of our
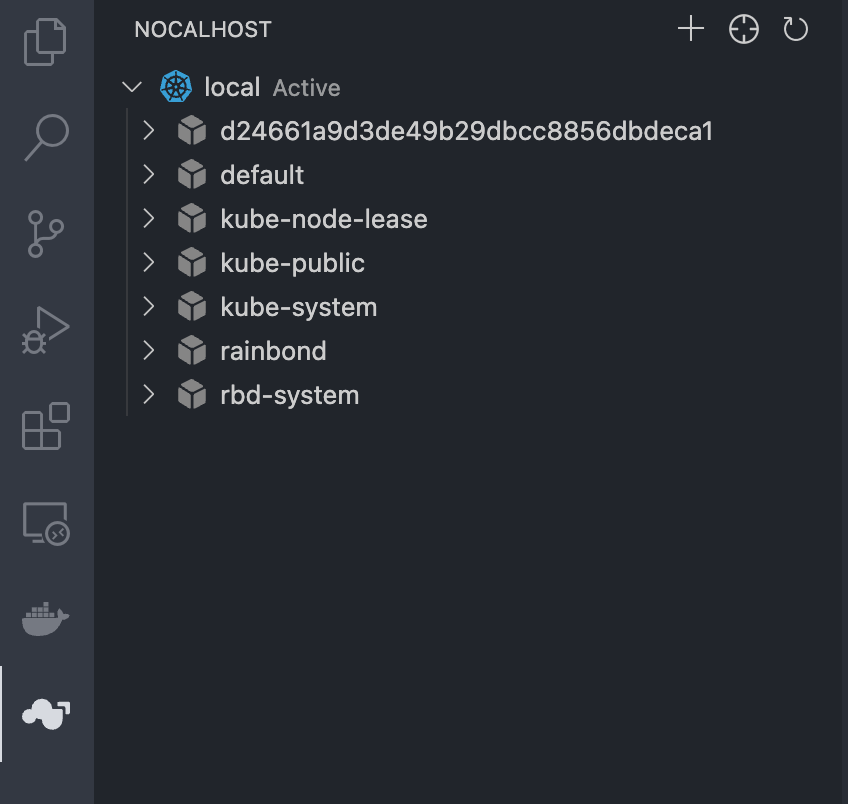
kubeconfigfile, and click Add Cluster to add a cluster. -
After the addition is complete, as shown in Figure:
4.4 Deploying Spring Cloud Microservices on Rainbond
-
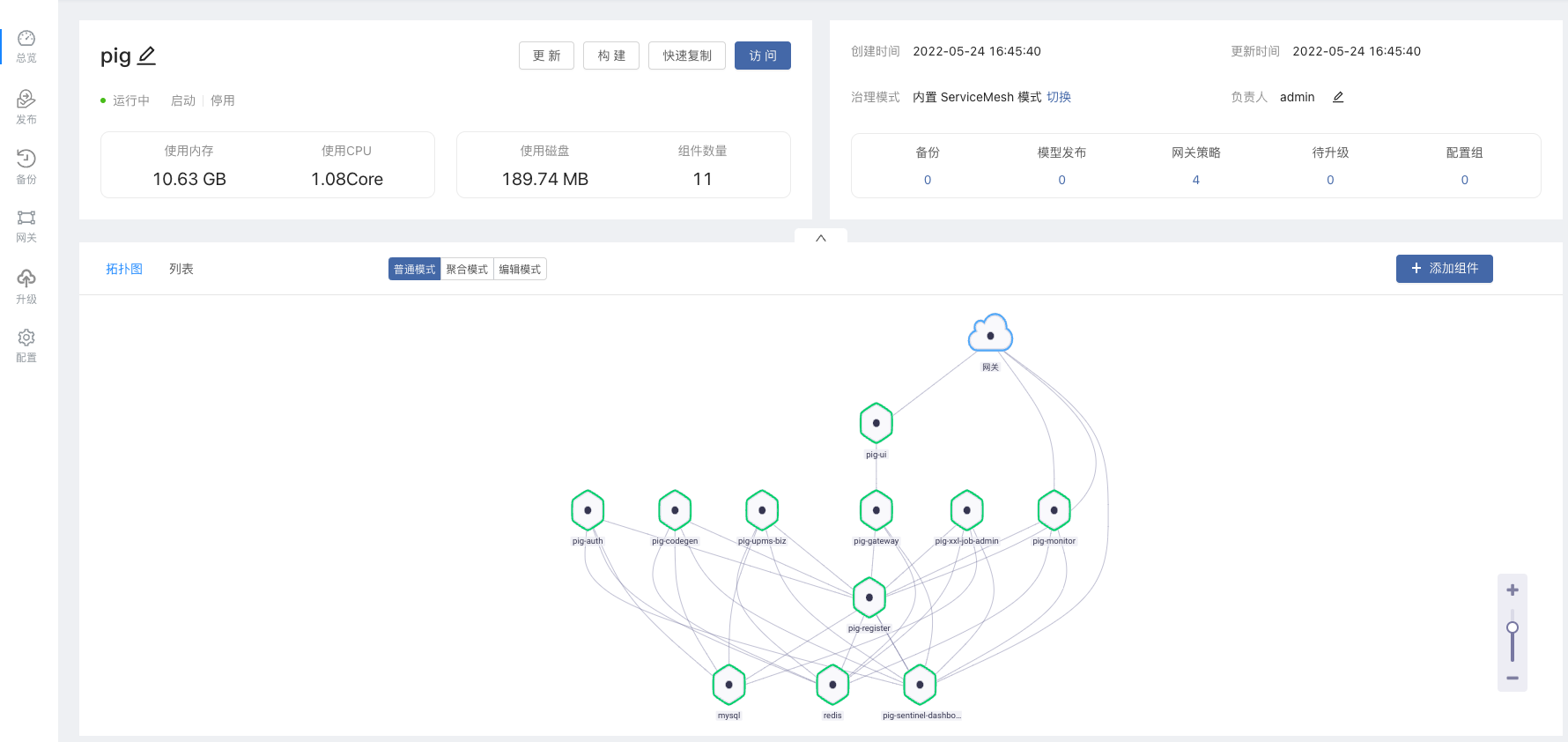
Here, choose to install the Spring Cloud Pig microservice component from the open source application store, and search for Pig in the application store to install it.
-
After the deployment is complete, the effect is as follows:
4.5 Enter Nocalhost development mode
Above, we have connected the cluster in the local Vscode, and have also installed the Spring Cloud Pig microservice in Rainbond, then we will select one of the components in the local Vscode for development. Here, in order to make the effect more obvious, choose to develop pig-ui component.
4.5.1 Clone Pig-ui code to local
git clone https://gitee.com/zhangbigqi/pig-ui
4.5.2 Start local development
Open Vscode, click button , and find our Pig-ui component. Since the application is installed from the open source application store, the Deployment name is an automatically generated string, and we need to query it in the component.
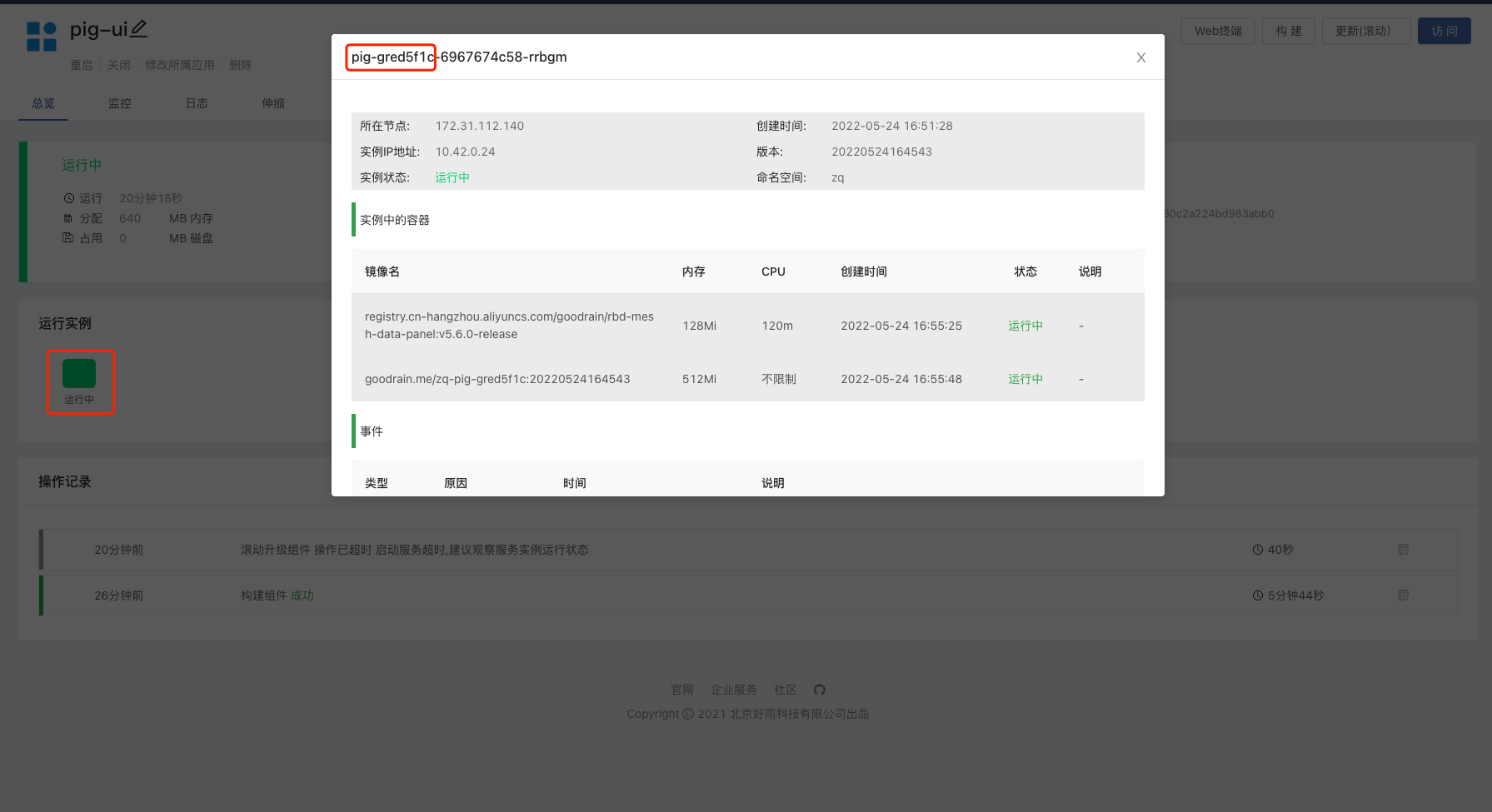
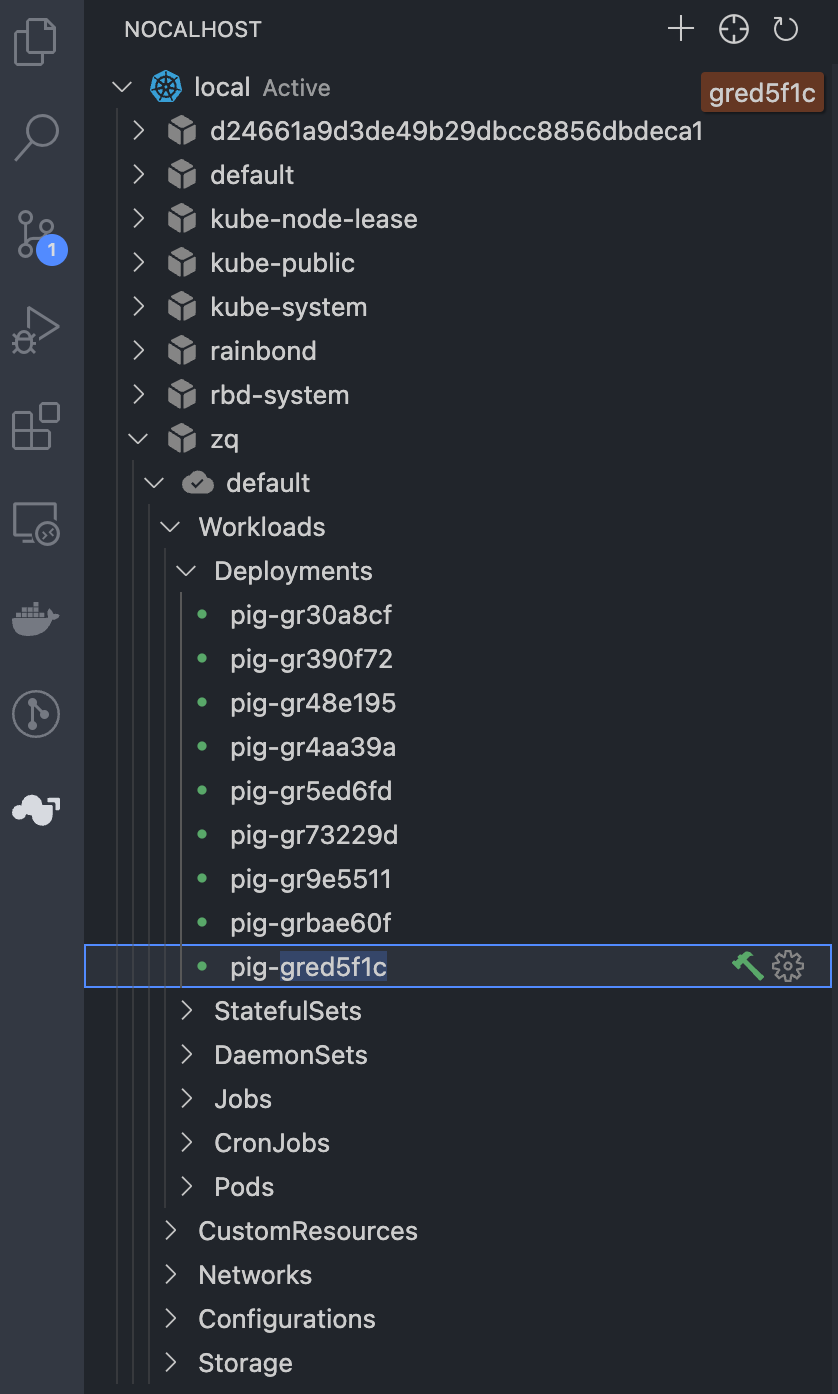
We click 🔨 next to it to enter the development mode,
- Prompt to select a container, we choose the container
gred5f1c, the remaining container is Rainbond's Mesh container, which is used for internal communication and cannot be replaced. - Prompt to specify the source code directory, select the code directory we just cloned.
- After waiting for a while, the terminal interface of the remote container will be opened by default and the files in the container will be synchronized with the local in real time, as follows:
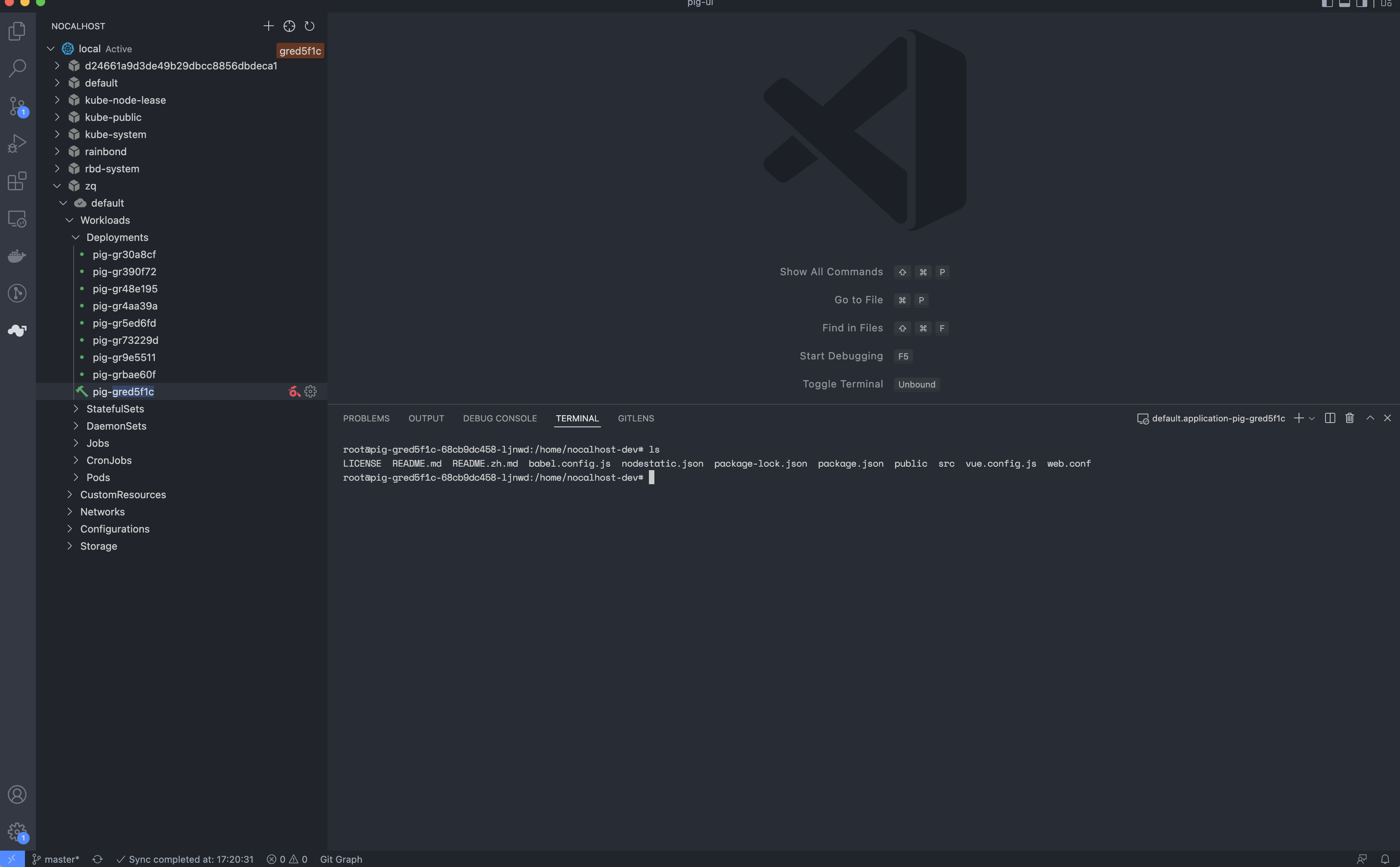
4.5.3 Start the project
-
Install project dependencies, execute
npm install -
run the project
npm run dev
After startup, the effect is as follows, the port in the container is 80

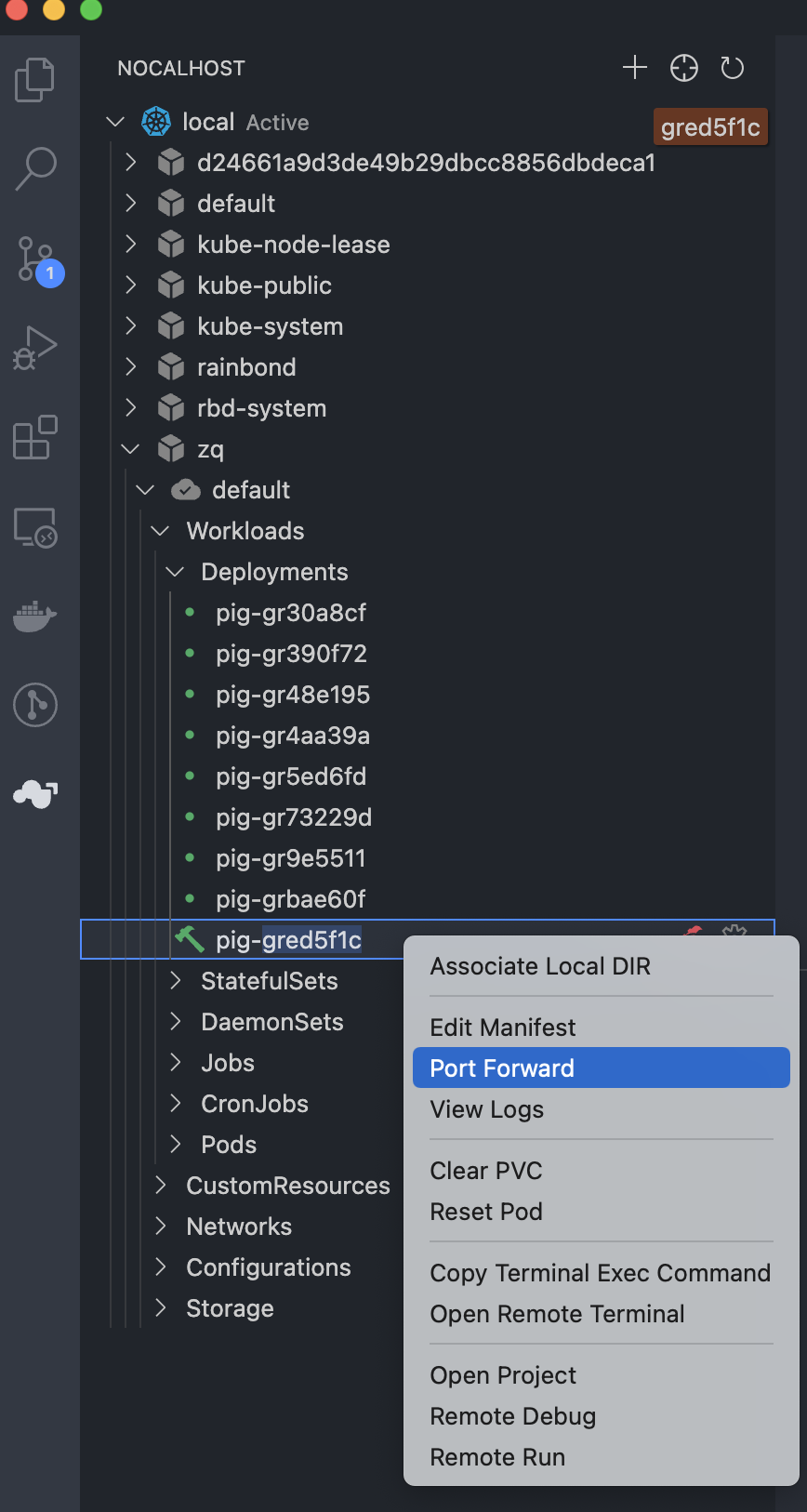
- Turn on port forwarding, click button
, find our Deployment, right-click to select Port Forward, Add Port Forward, enter
38000:80to forward the container's port 80 to the local port 38000.
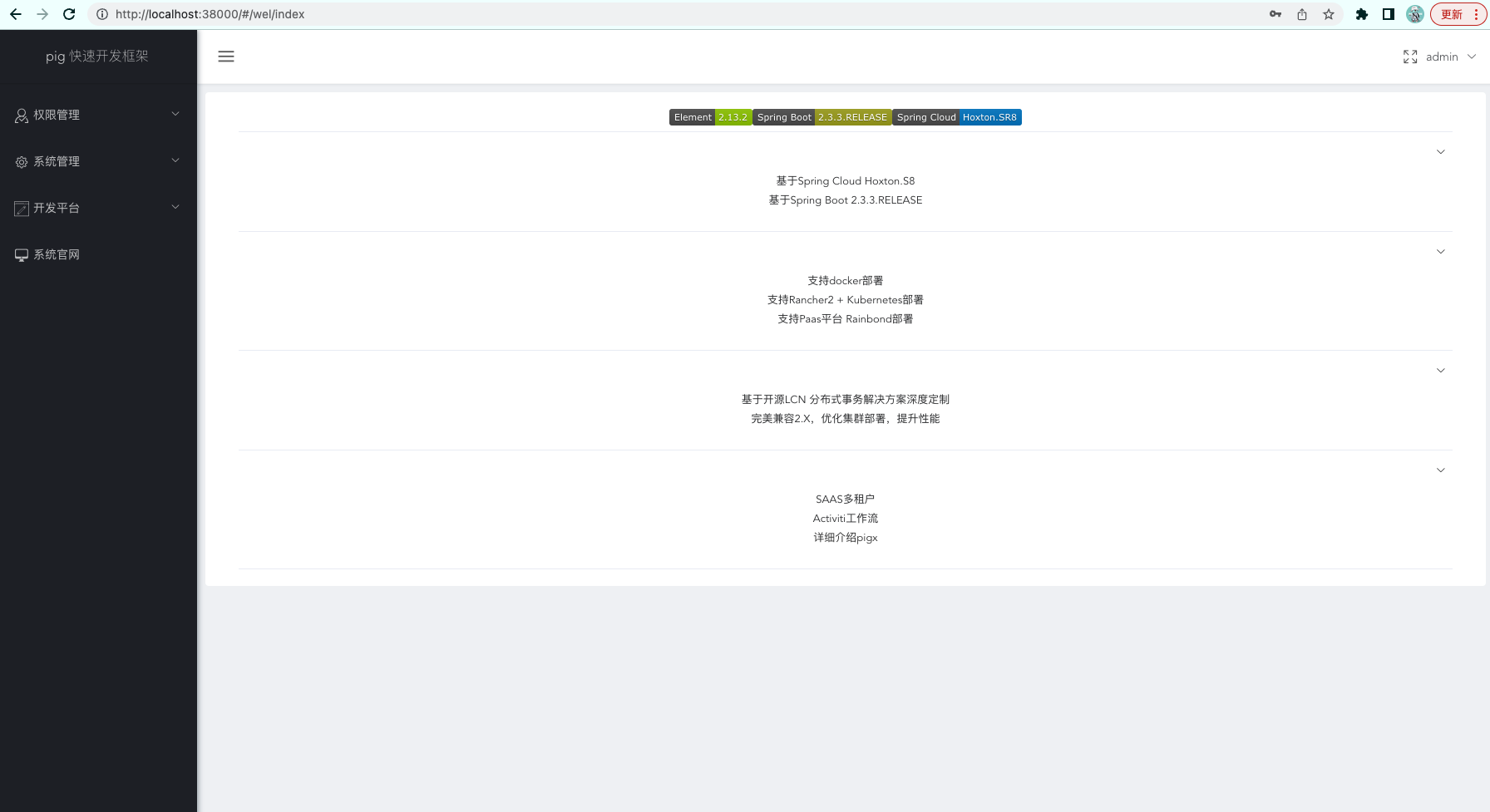
- The page can be accessed through
http://localhost:38000, and you can also log in normally.
4.5.4 Modify the code to check the effect
The above has demonstrated that if the service in the remote container is accessed locally, let's modify the code to see the effect.
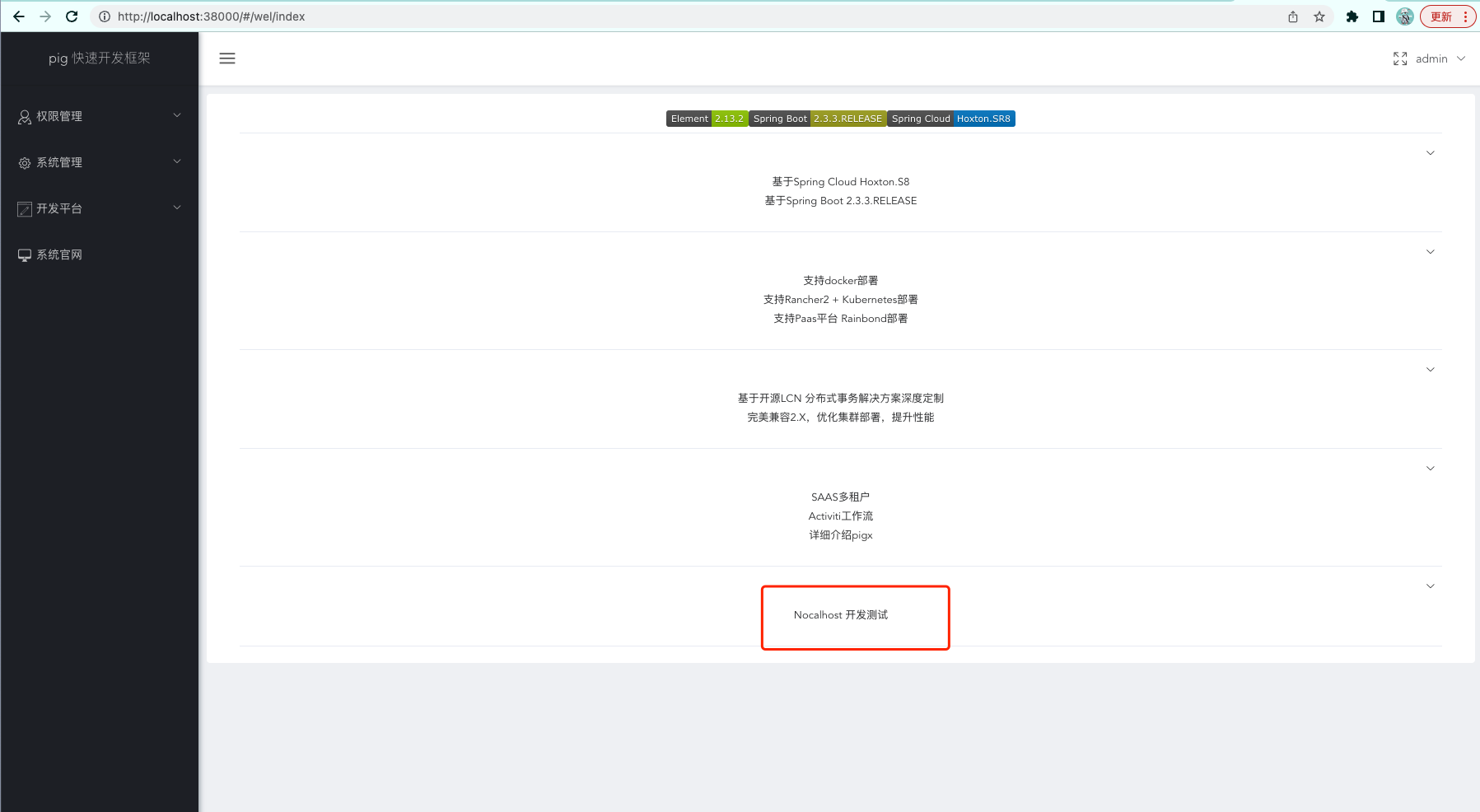
Modify src/page/wel.vue, add a piece of code, save it.It can be found that when we save, the terminal is automatically restarted, which is consistent with the local development effect.
Modifications to files are synced to the container in real time.
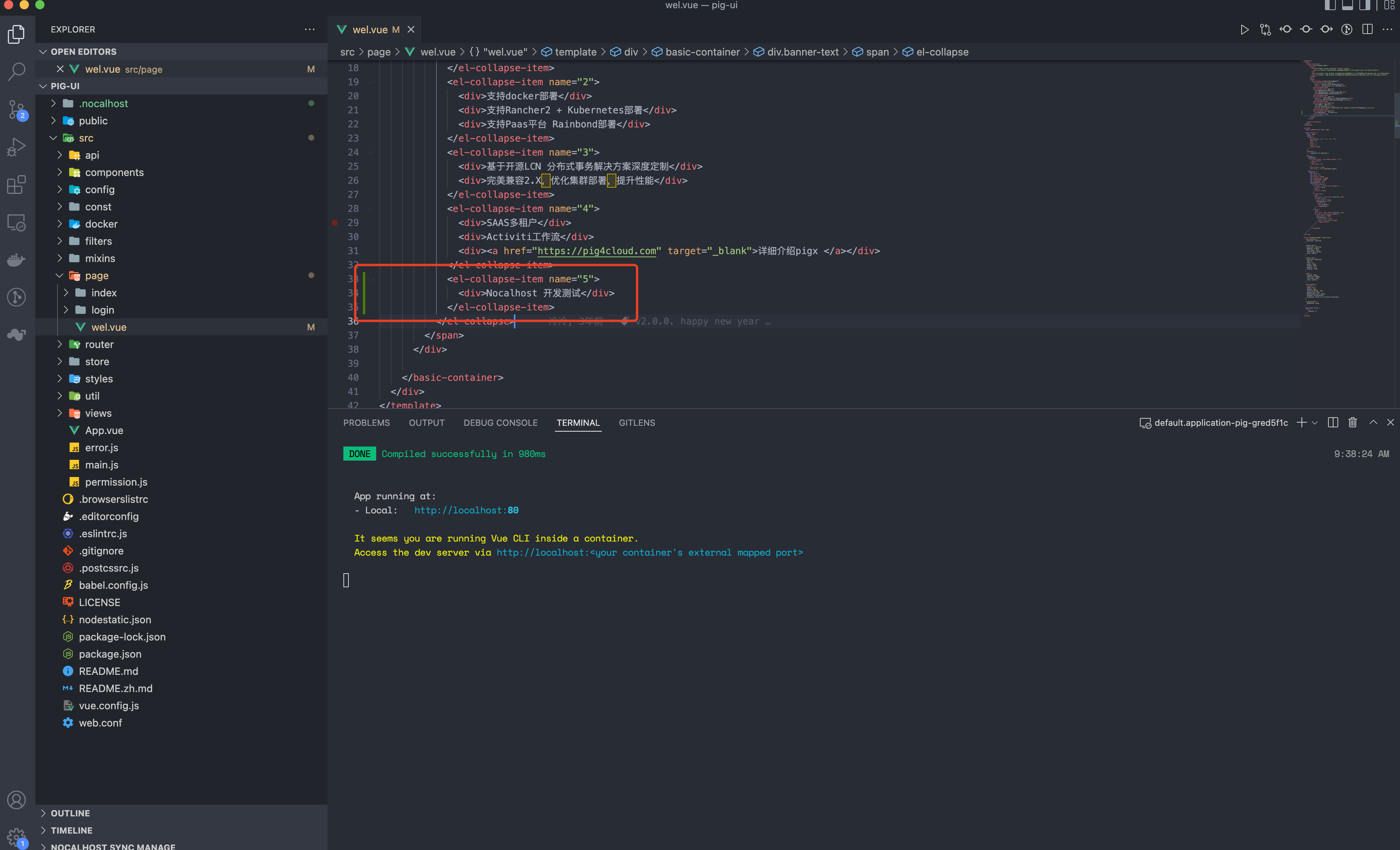
Refresh pagehttp://localhost:38000, you can see that the modified content has taken effect.
write at the end
Through the above practical steps, we have been able to develop microservice applications on Rainbond through Nocalhost, get rid of local development, and enter cloud-native rapid development to improve our development efficiency.
This article only introduces the basic development, you can also configure Nocalhost development configuration for the project, etc. Friends can explore by themselves.