High Availability Cluster Description
The key to deploying a high availability cluster lies in planning, such as: how many servers the entire cluster plans to use, what the role of each server is, how server resources and disks are planned, etc.
Deployment Architecture
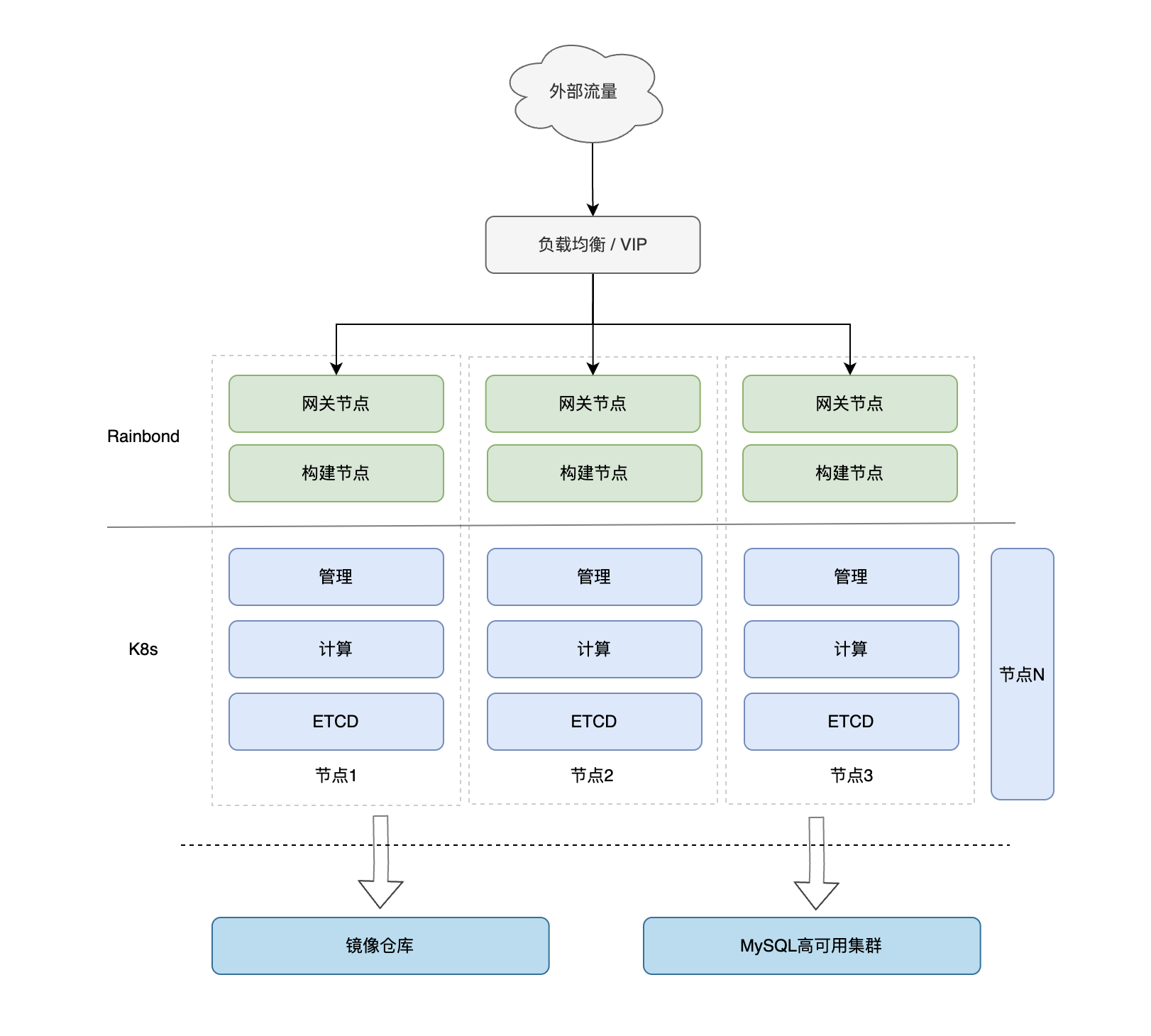
As shown in the figure: the minimum number of nodes (3 nodes) is used to ensure high availability, K8s uses multiple Master + multiple ETCD clusters to ensure high availability, and Rainbond uses external load balancing + multiple gateway nodes + MySQL high availability cluster to ensure high availability.
High Availability Kubernetes Cluster
The Kubernetes cluster needs to deploy at least a 3-node cluster, and the attributes of the 3 nodes can be reused, for example: 3 management nodes, 3 compute nodes, 3 ETCD nodes.
You can install the Kubernets cluster by yourself, or you can install the Kubernetes cluster through Rainbond.
High Availability Rainbond Cluster
The key to deploying a high availability Rainbond cluster lies in:
- High availability Kubernetes cluster;
- Rainbond cluster's advanced configuration uses external high availability services.
The following will explain the external services required by Rainbond separately, including the high availability deployment of these services.
Load Balancing
Rainbond cluster gateway needs to be deployed on a high availability load balancer to ensure the high availability of the cluster gateway.
Use existing load balancer
If there is already a high availability load balancer, it can be used directly, provided the following conditions are met:
- Proxy to all gateway nodes of Rainbond
- Open ports 80, 443, 6060, 7070, 8443
Deploy Keepalived
If there is no load balancing service yet, the high availability of the gateway can be ensured by deploying Keepalived service on the gateway node. In this way, the gateway nodes are in a master-backup relationship.
Gateway Node
Specify which node the Rainbond gateway service is deployed and runs on. The gateway service on each node can work independently. Even if one gateway node goes down, other gateway nodes can still work normally.
Build Node
Specify which node the Rainbond build service is deployed and runs on. The more build nodes there are, the more tasks can be built in parallel at the same time.
Building consumes a lot of disk space. It is recommended to run the build service on nodes with SSD disks.
Image Repository
Specify the underlying image repository of Rainbond. All component images on the platform will be pulled and pushed from this repository.The default built-in image repository is provided, running in the rbd-system namespace as a Pod, and the default metadata is stored through the rbd-hub pvc.
If you already have an image repository, you can use it directly, provided the following conditions are met:
- It is recommended to use the https protocol and trusted certificates. If http is used, the configuration related to Docker and Containerd needs to be modified.
MySQL
Rainbond needs to use MySQL to store console and cluster data.The default built-in MySQL database is provided, running in the rbd-system namespace as a Pod, and will randomly bind to a node and store the metadata in the /opt/rainbond/data/dbxxx directory of the node.
If you already have a high availability database, you can use it directly, provided the following conditions are met:
- The database version is MySQL 5.7, 8.0;
- Create the console region library in advance;
- The database character encoding is utf8mb4;
- It is recommended that the database and Rainbond cluster network are in the same intranet range.
If the database has not been installed yet, please refer to the documentation to install Deploy MySQL master-slave cluster in Docker, Deploy MySQL master-slave cluster in Centos 7